Welcome to our Google Ads tutorial. We will guide you through everything you need to know about Google Ads with our videos and our articles. We start by answering some common questions, then you can follow our Google Ads search campaign tutorial and then our Google Display Ads tutorial. You will find even more videos and articles so you can learn everything from conversion tracking to keyword targeting to attribution models.
About Google Ads
Paid advertising is important for every business owner. Google offers an advertising platform to business owners called Google Ads, which can be really beneficial for the growth of your business. The Google Ads platform was formerly known as Google AdWords. It allows advertisers to run search ads, display ads, product listing ads, mobile app ads, and video ads. Advertisers can target certain keywords on the Google Search Network, and their ads will show up in the Google Search Results.
What is Google Ads?
Google Ads is an advertising platform, which is made up of the Google search engine, search partners, the Google Display Network, Audiences, Websites, Videos, YouTube channels, Mobile apps, and more. Advertisers can utilize Google Ads to drive targeted traffic to their website, which can help increase conversions such as leads and sales.
Google Ads is a Pay-Per-Click (PPC) advertising platform, where advertisers pay per click (or impression) on an ad.
Google Ads is an effective way to drive qualified traffic, or good-fit customers, to your business because they’re searching for products and services like the ones you can boost your website traffic, receive more inquiries, and increase in-store visits.
Over time, Google Ads will also help you analyze and optimize those ads to reach more people.
How Does Google Ads Work?
First of all, you have to set up a Google Ads campaign. The next thing you should do is choose the most relevant keywords for your business. There are helpful free keyword research tools like the Google Keyword Planner. In addition, you should think carefully about words and phrases that your potential customers will use when they start searching for your products and/or services.
The main purpose of Google Ads is to match your keywords with the ads and landing pages that you create. Then, your ad may show up while somebody is searching for your targeted words and terms. On the Display Network, your ads can appear based on your targeted audiences or websites that are related to your business.
How do Google Search Ads Work?
When it comes to search network campaigns, Advertisers target and bid on keywords that they want to match to potential customer’s search terms. Advertisers can create ads and landing pages that match closely to their targeted keywords. Advertisers are charged when people click on their advertisements. Advertisers are not charged unless someone actually clicks on their ad. This is one major method that Google uses to earn revenue because the advertisers must pay for these clicks.
Before you start creating Google Search Ads Campaigns, you have to make sure you understand the basics – the bidding process, how Quality Score works, how to set-up Campaigns and Ad Groups, how to create ads, landing pages, and how cost-per-click works.
How Does the Google Ads Auction Work?
How does Google Ads determine which ads will show up when someone starts a search on Google? There is an ad auction that determines in what order the ads will appear. There are two major factors that influence the Google Ads auction: Your bids and quality scores. Google looks at your the bids and quality scores of every advertise entering the ad auction to determine Ad Rank.
What is Google Ads Ad Rank?
Ad Rank is determined by an advertiser’s bid and their quality score at auction time. The ad auction occurs every time someone searches in Google. Google is able to look at the quality of each advertiser’s ads and their bids instantaneously for every search term that triggers advertisements.
- Bids: You have to set your bids and tell Google the maximum amount of money you agree to pay for a click on your ad. Google Ads has developed smart bidding strategies like Enhanced CPC, Target Return on Ad Spend (Target ROAS), and Target Cost-Per-Action (Target CPA), which allows advertisers to set automated bids that are focused on conversions and conversion value.
- Quality Scores: Another thing that has an impact on the action is the quality of your ads. This quality is summarized in your Quality Score. Quality Score is made up of your Ad Relevance, Expected Click-Through Rate, and Landing Page Experienced. Essentially, Google Ads looks at the overall quality and relevancy of ads and landing pages based on a user’s search query.
How Do Google Display Ads Work?
Advertisers can use audience targeting or content targeting to reach people as they browse specific websites, watch YouTube videos, or use mobile apps. The Google Display Network allows advertisers to target relevant audiences as they browse the internet. Your display ads can drive traffic back to relevant landing pages on your website that sell your products and services.
Where do Google Ads Show?
There is a major different between paid ads and organic search results. Google Ads appear on the top or the bottom of the Google search results. The ads are ranked according to the Ad Rank factors above.
What is the Google Search Network?
The Google Search Network is where your search ads will appear. It is made up primarily of the Google Search Engine and a large group of websites with search engines that will display Google search ads. When you start advertising on this network, your ads will show up next to search results on Google and Google search partners.
The Google Search Network is effective because it succeeds in targeting an active searcher. The network is able to connect advertisers and people who are actively looking for products and services. On average, the Google Search Network drives more conversions and a higher conversion rate than the Google Display Network.
How Much Does Google Ads Cost?
Costs are calculated based on your targeting and overall competition. An advertisers keyword bids, budget, competition, audience targeting, and keyword quality scores are all major cost factors. If you are targeting expensive and competitive keywords, they can cost upwards of $10-$20 per click. Those are highly competitive words in industries such as law, insurance, banking, and marketing, which have high lifetime values. However, most advertisers will spend anywhere from $0.50-$3.00 per click depending on their industry and targeting.
Advertisers have complete control over their budgets and they can optimize their campaigns over time to lower costs.
How to Use Google Ads Successfully?
If you want to succeed in using this advertising platform, you have to use keyword research tools such as the Google Keyword Planner to find relevant and popular keywords for your business. From there, you need to test and optimize your Campaign, Ad Groups, Keywords, Audience, Ads, and Landing Pages. Google Ads is considered immensely effective for all kinds of businesses, but it requires testing and optimization.
Should You Use Google Ads?
I belive that paid online advertising is essential for the growth of any business. Even if your budget is not that high, you should definitely try usng Google Ads and increase your chances of getting more customers. Any business that sells a product or a service should at the very least test Google Ads because you can reach customers who are actively seeking your business. Lastly, you can see whether or not Google Ads is driving you a positive Return On Ad Spend (ROAS) with conversion tracking.
Google Ads Terms to Know
- Ad Extensions
- AdRank
- Bidding
- Campaign Type
- Click-Through Rate
- Conversion Rate
- Display Network
- Impression
- Keywords
- PPC
- Quality Score
1. Ad Extensions
Ad Extensions allow you to supplement your ad with additional information at no extra cost. These extensions fall under one of five categories: Sitelink, Call, Location, Offer, or App.
2. AdRank
Your AdRank determines your ad placement. The higher the value, the better you’ll rank, the more eyes will fall on your ad, and the higher the probability of users clicking your ad. Your AdRank is determined by your maximum bid multiple by you Quality Score.
3. Bidding
Google Ads is based on a bidding system, where you, as the advertiser, select a maximum bid amount you’re willing to pay for a click on your ad. The higher your bid, the better your placement. You have three options for bidding: CPC, CPM, or CPE.
- CPC, or cost-per-click, is the amount you pay for each click on your ad.
- CPM, or cost per mille, is the amount you pay for one thousand ad impressions; that is when your ad is shown to a thousand people.
- CPE, or cost per engagement, is the amount you pay when someone takes a predetermined action with your ad.
And, Yes, we’ll review bidding strategies below.
4. Campaign Type
Before you begin a paid campaign on Google Ads, you’ll select between seven campaign types: search, display, video, shopping, app, smart, or performance max.
- Search ads are text ads that are displayed among search results on a Google results page.
- Display ads are typically image-based and are shown on web pages within the Google Display Network.
- Video ads are between six and 15 seconds and appear on YouTube.
- Shopping campaigns appear on search results and the Google shopping tab.
- App campaigns use information from your app to optimize ads across websites.
- Smart campaigns have Google finding the best targeting to get you the most bang for your bunk.
- Performance Max is a new campaign type that lets advertisers access all Google Ads inventory from a single campaign.
5. Click-Through Rate (CTR)
Your CTR is the number of clicks you get on your ad as a proportion of the number of impressions your ad gets. A higher CTR indicates a quality ad matching search intent and targeting relevant keywords.
6. Conversion Rate (CVR)
CVR is a measure of form submissions as a proportion of total visits to your landing page. Simplistically speaking, a high CVR means that your landing page presents a seamless user experience that matches the ad’s promise.
7. Display Network
Google ads can be displayed on either search results pages or a web page within Google’s Display Network (GDN). GDN is a network of websites that allow space on their web pages for Google Ads – these ads can be text – or image-based and are displayed alongside content relevant to your target keywords. The most popular Display Ad options are Google Shopping and app campaigns.
8. Impressions
Every Time your ad is shown on the SERP, it receives an impression. Some advertisers and marketers like to refer to this informally as “eyeballs” on the ad.
impressions make up one-half of the CTR equation we mentioned above.
You can use this insight from impressions to understand how many people who see your ad are clicking through to your landing page and optimize your ad to get a higher CTR.
Keep in mind that it’s virtually impossible to have all impressions convert to clicks and achieve a 100% CTR. People may click on an organic search result instead of clicking your ad.
9. Keywords
When a Google user types a query into the search field, Google returns a range of results that match the searcher’s intent. Keywords are words or phrases that align with what a searcher wants and will satisfy their query. You select keywords based on which queries you want and will satisfy their query. You select keywords based on which queries you want to display your ad alongside. For example, a searcher that types “how to clean gum off shoes” will see results for advertisers that targeted keywords like “gum on shoes” and “clean shoes.”
Negative keywords are a list of keyword terms that you do not want to rank for. Google will pull you from the bid on these keywords. Typically, these are semi-related to your intended search terms but fall outside of the realm of what you offer or want to rank for.
10. PPC
Pay-Per-Click, or PPC, is a type of advertising where the advertiser pays per click on an ad. PPC is not specific to Google Ads, but it is the most common type of paid campaign. It’s important to understand the ins and outs of PPC before launching your first Google Ads campaign.
11. Quality Score (QS)
Your Quality Score measures the quality of your ad by your click-through rate (CTR), the relevance of your keywords, the quality of your landing page, and your past performance on the SERPs. QS is a determining factor in your AdRank.
Factors That Influence Google Ads
Many factors impact your ability to create effective and high-performing Google Ads. Let’s cover them below.
AdRank
AdRank determines the placement of your ads. It’s determined by a formula that takes into account Quality Score and the amount you bid on a keyword.
Quality score is based on the quality and relevance of your ad, and Google measures that by how many people click on your ad when it’s displayed – i.e., your CTR. Your CTR depends on how well your ad matches searcher intent, which you can deduce from three areas:
- How relevant your keywords are
- Whether your ad copy and CTA meet the searcher’s intent
- The user experience of your landing page
Your quality score is where you should focus most of your attention when you first set up your Google Ad campaign – even before you increase your bid amount. The higher your QS, the lower your acquisition costs will be and the better placement you’ll get without having to pay more money.
Location
When you first set up your Google ad, you’ll select a geographical area where your ad will be shown. If you have a storefront, this should be within a reasonable radius around your physical location.
Your location settings will play a role in placement. For instance, if you own a yoga studio in San Francisco, someone in New York that enters “yoga studio” will not see your result, no matter your AdRank. That’s because Google’s main objective is to display the most relevant results to searchers.
Keywords
Keyword research is just as important for paid ads as it is for organic search. Your keywords need to match searcher intent as much as possible. That’s because Google matches your ad with search queries based on the keywords you selected.
Each ad group that create within your campaign will target a small set of keywords (one to five keywords is optimal), and Google will display your ad based on those selections.
Match Types
Match Types give you a little wiggle room when it comes to your keyword selections – they will Google whether you want to match a search query exactly or if your ad should be shown to anyone with a search query that’s semi-related.
There are four match types to choose from:
- Broad Match is the default setting that uses any word within your keyword phrase in any order. For example, “goat yoga in Oakland” will match “goat yoga” or “yoga Oakland”.
- Modified Broad Match allows you to lock in certain words within a keyword phrase by denoting them with a “+” sign. Your matches will include that locked-in word at the very least. For example, “+goats yoga in Oakland” could yield “goats,” “goats like food,’ or “goats and yoga.”
- Phrase Match will match with queries that include your keyword phrase in the exact order but may include additional words before or after it. For example, “goat yoga” can yield “spotted goat yoga” or “goat yoga with puppies.”
- Exact Match maintains your keyword phrase as it is written in the exact order. For example, “goat yoga” will not show up if someone types “goats yoga” or “goat yoga class.”
If you’re just starting out and don’t know precisely how your persona will be searching, move from a broad match to a more narrow approach so you can test which queries yield the best results. However, since your ad will be ranking for many queries (some unrelated), you should keep a close eye on your ads and modify them as you can gain new information.
Headline and Description
Your ad copy can be different between a click on your ad and a click on your competitor’s ad. Therefore, it’s important that your ad copy matches the searcher’s intent, is aligned with your target keywords, and addresses the persona’s pain point with a clear solution.
To illustrate what we mean, let’s review an example.
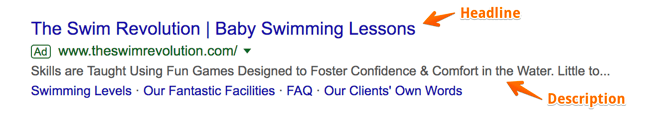
A search for “baby swim lessons” yielded this results. The copy is concise and uses limited space wisely to convey its message and connect with its target audience.
The Swim Revolution knew to put the keyword in their headline, so we instantly know that this ad matches what we’re looking for. Furthermore, the description tells us why this is the best option for swim lessons because it addresses the concerns of their persona – a parent looking to enroll their baby in a swim class.
They use words like “skills,” “fun,” “confidence,” and “comfort in the water” to ease our nerves about putting a baby in a pool and to prove to us that we will get what we want out of this class – an infant that can swim.
This kind of ad copy will get you clicks, but conversions will result from carrying this level of intention into your landing page copy.
Google Ads Best Practices
If you’ve tried unsuccessfully to advertise on Google, don’t give up. There are many reasons why your Google Ads could be underperforming. But, first, let’s cover some standard Google Ads best practices.
1. Use a PPC Planning Template 
Using a lanner keeps your PPC projects organized. With Google and HubSpot’s PPC Planning Template, you can view how your ads will appear online, see your character counts, and manage your campaigns all in one place.
2. Avoid broad keyword terms
You really need to nail it for your keywords, which is why testing and tweaking should be a part of your strategy. If your keywords are too broad, Google will be placing your ad in front of the wrong audience, which means fewer clicks and a higher ad spend.
Review what’s working (i.e., which keywords generate clicks) and adjust them to best match your ads with your target audience. You likely won’t get the mix right the first time, but you should keep adding, removing, and tweaking keywords until you do.
3. Don’t run irrelevant ads
If your ad doesn’t match the searcher’s intent, you won’t get enough clicks to justify your ad spend. Your headline and ad copy need to match the keywords you’re bidding on, and the solution your ad is marketing needs to solve whatever pain point that searcher is experiencing.
It’s a combination that will yield the results you’re looking for, and it may just be a few tweaks away. You have the option to create multiple ads per campaign – use this feature to split-test which ads work best. Or, better yet, use Google’s Responsive Search Ads feature.
4. Improve your Quality Score (QS)
Your Quality Score (QS) is how Google determines how your ad should rank.
The higher your QS, the better your rank and placements on the Search Engine Results Page (SERP). If your quality score is low, you’ll have fewer eyeballs on your ad and fewer chances to convert.
Although Google lets you know your Quality Score, it’s your responsibility to improve it.
5. Optimize your ad landing page
Your efforts shouldn’t stop with your ad – the user experience after a click is equally essential.
What does your user see once they click your ad? Is your landing page optimized for conversions? Does the page solve your user’s pain point or answer their question? Your user should experience a seamless transition through the conversion process.
Google Ads Tips
Now that you know how to use and set up a Google Ad campaign, here are a few short tips or best practices to follow to help you create successful campaigns.
We’ve covered these at length throughout this post, but their importance can’t be overstated. Use this as a checklist you can refer to again and again.
1. Have a clear goal
It’s vital to define your objectives before you create your ad, instead of creating an ad first and then tweaking it to fit your objectives. Sit down with your marketing team to prepare an advertising plan and create SMART goals for your Google Ads campaigns.
2. Create a relevant landing page
When prompted to add your URL when creating your ad, ensure that the URL you provide leads to a relevant landing page. If your ad is interesting enough to get clicked, you could undo all that great work if it directs them to a poor landing page.
Therefore, optimize your landing pages so that your ad will help convert a curious visitor into a paying customer. Check out our landing page guide so you know exactly how to create great landing pages.
3. Use the right keywords
Keywords are super important, so it’s only right that you choose the best ones for your ad.
Long-tail keywords are some of the best types of keywords because they are very specific and can target one business.
For example, say you run a cat clinic. A generic keyword like ‘cat clinic’ won’t target people in your area, but something like ‘cat clinic in belvedere’ is more likely to attract the right audience.
4. Automate the process
you can maximize conversion by optimizing the bidding process. Tools like Smart Bidding can increase or reduce bids for you, depending on the chance of success.
Therefore, you’ll spend money only when there’s a higher chance of success.
5. Use Ad Extensions
Extensions can take your ad performance up a notch. These extensions allow you to specify your locations, services, goals, or sales promotions.
For example, you could include a telephone number in your ad so people can call you to inquire about your services right away.
6. Use negative keywords
Google Ads allows you to include negative keywords. Using these keywords indicates what your product or service is not, thus preventing you from showing up in irrelevant SERPs.
Using the cat clinic example, you might only cater to cats and not dogs or other pets. In this case, you can exclude terms like ‘dogs’ and other qualifiers.
7. Measure and improve upon your strategy
When you integrated your ads with Google Analytics, you can track important metrics like page popularity, the keywords that drive the most traffic, and more.
Collecting and analyzing these and other metrics will help you improve the quality of your ads, boost your conversions, and increase revenue over time.
Additional Resources to Optimize Your Google Ads
Your ad copy headline is not the only component that will make your paid campaign successful. Getting a user to click is only the beginning… they should arrive on a landing that’s optimized for conversion and then be taken to a Thank You page that tells them what to do next.
If you want your Google Ads to produce qualified leads and customers, then check out these additional resources and use them as guidelines as you set up your Google Ads campaign.
- Landing Page Best Practices will teach you how to set up a landing page that’s prime for conversions so you don’t waste those precious clicks.
- Optimized “Thank You” Pages shows you what to do with your new lead post-conversion, how to keep them on your site, and ways to maintain their attention.
- Tips for Mobile Google Ads teaches you the key differences between desktop and mobile ads and how to optimize both.
- Optimizing Google Ads Costs will show you how we, at HubSpot, maximize our Google Ads spend to get the ROI.
- Quality Google Ads Examples That Convert shares examples of Google advertising campaigns that got it right.
Steps-By-Step Google Ads Tutorial
Google Ads is a very difficult PPC Advertising channel to learn and understand. The step-by-step process below will help you get started as you create your first search campaign. One thing to keep in mind is that Google Display Advertising campaigns and YouTube Advertising campaigns are slightly different, but they are managed through the same interface.
Step 1 – Create Your Google Ads Account
- You want to start by creating your Google Ads Account.
You can use an existing Google Account to sign-up for your account. You will manage all of your advertisements in your account.
Step – 2 – Use The Full Version of Google Ads
- Avoid using Google Ads Express by clicking on the URL that says ‘Experienced with Google Ads?’
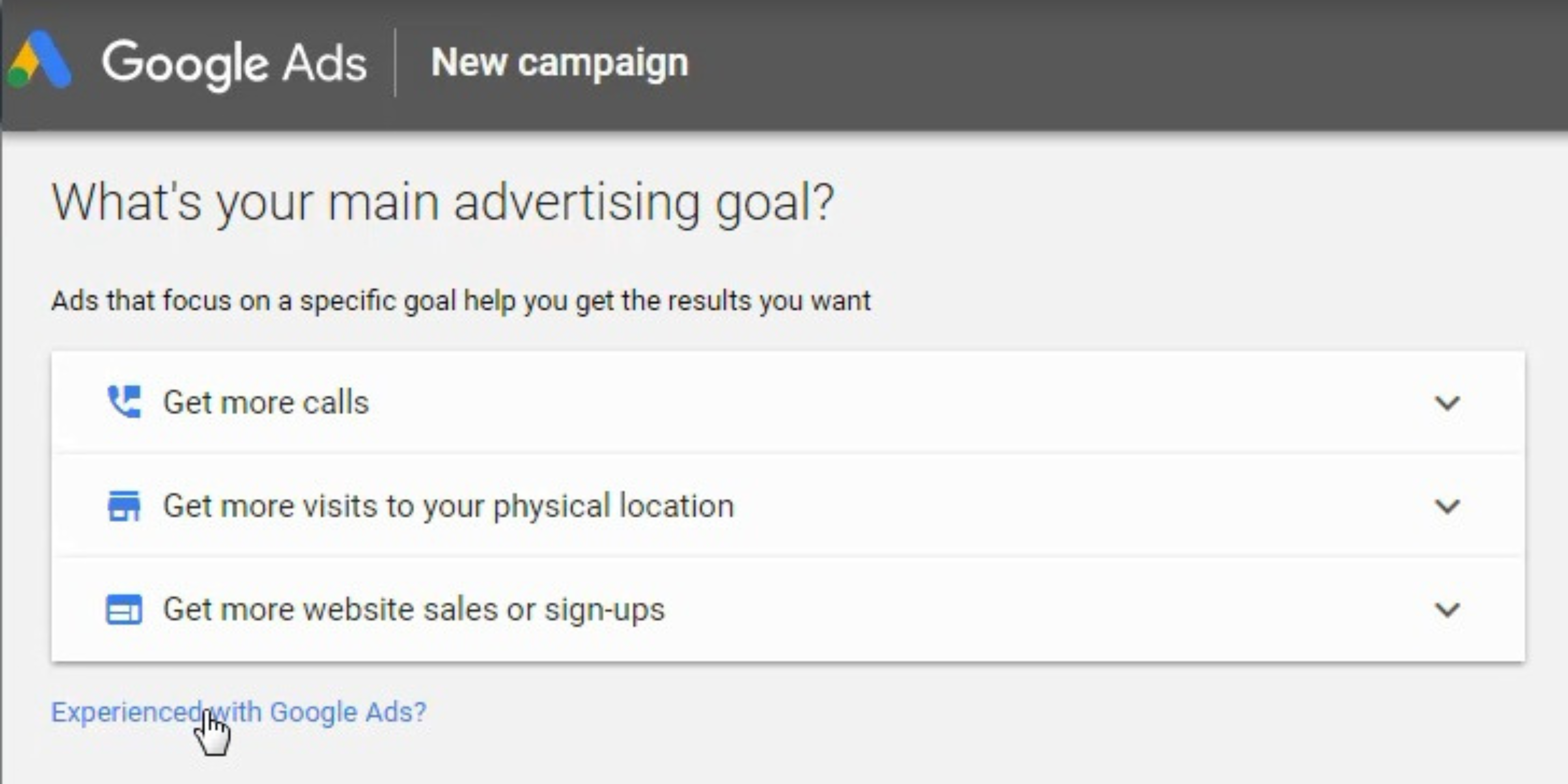
At the time of making this video and tutorial, Google will automatically opt you into Google Ads Express. You want to use the full version that Google offers. Another way to double-check this is by ensuring that the word ‘Express’ does not appear in the URL at the top.
Step 3 – Create An Account Without a Campaign
- Click on the link that says ‘Create an account without a campaign’ to get started in your account.
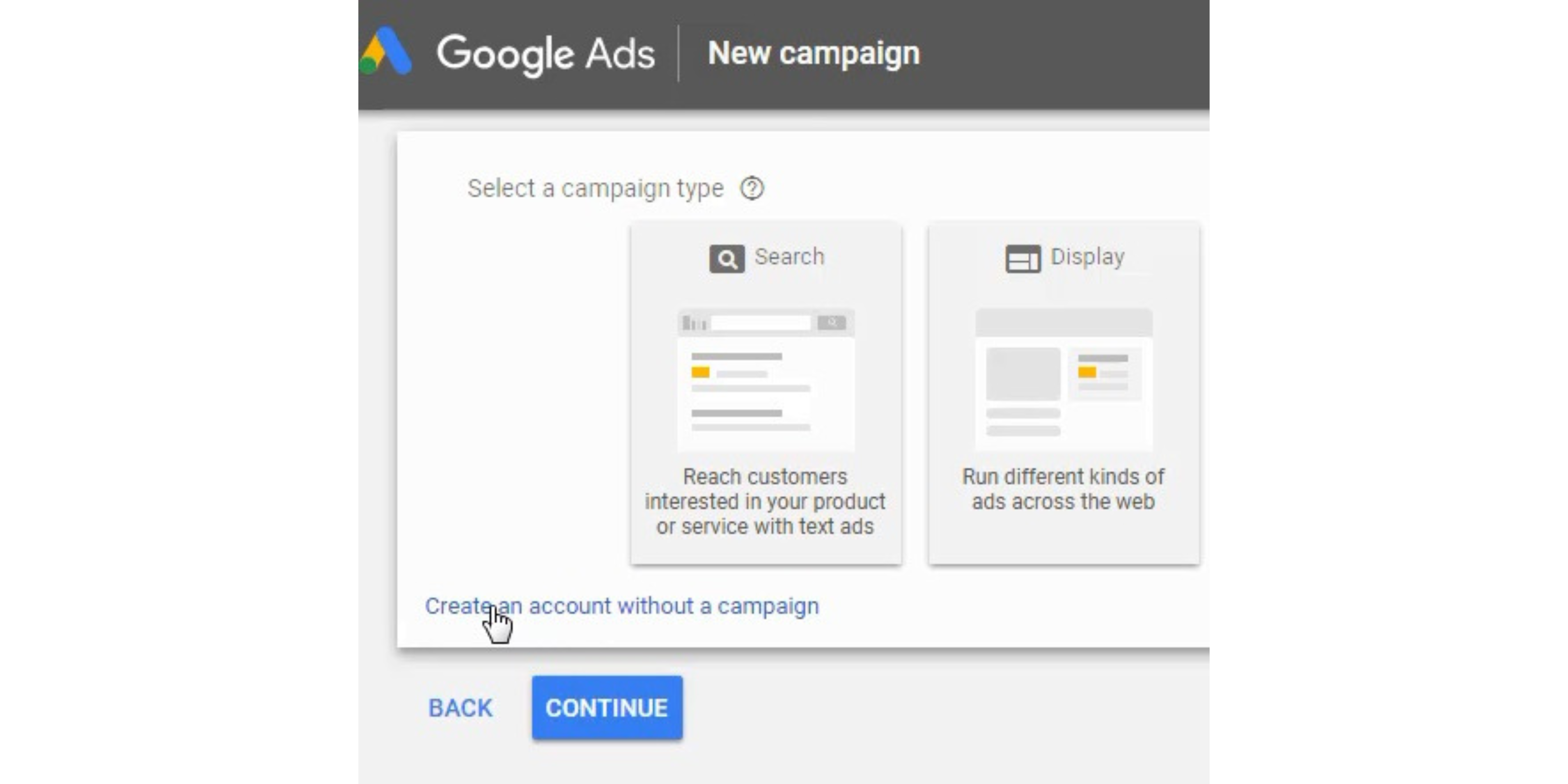
You can create your first search campaign during this step, but I prefer to set up conversion tracking first. That way, you can optimize your campaign for the conversions you import for your business.
Step 4 – Confirm Business Information and Explore Your Account
- Confirm your billing country, time zone, and currency. Then, click ‘Explore Your Account’ to reach the main Google Ads screen.
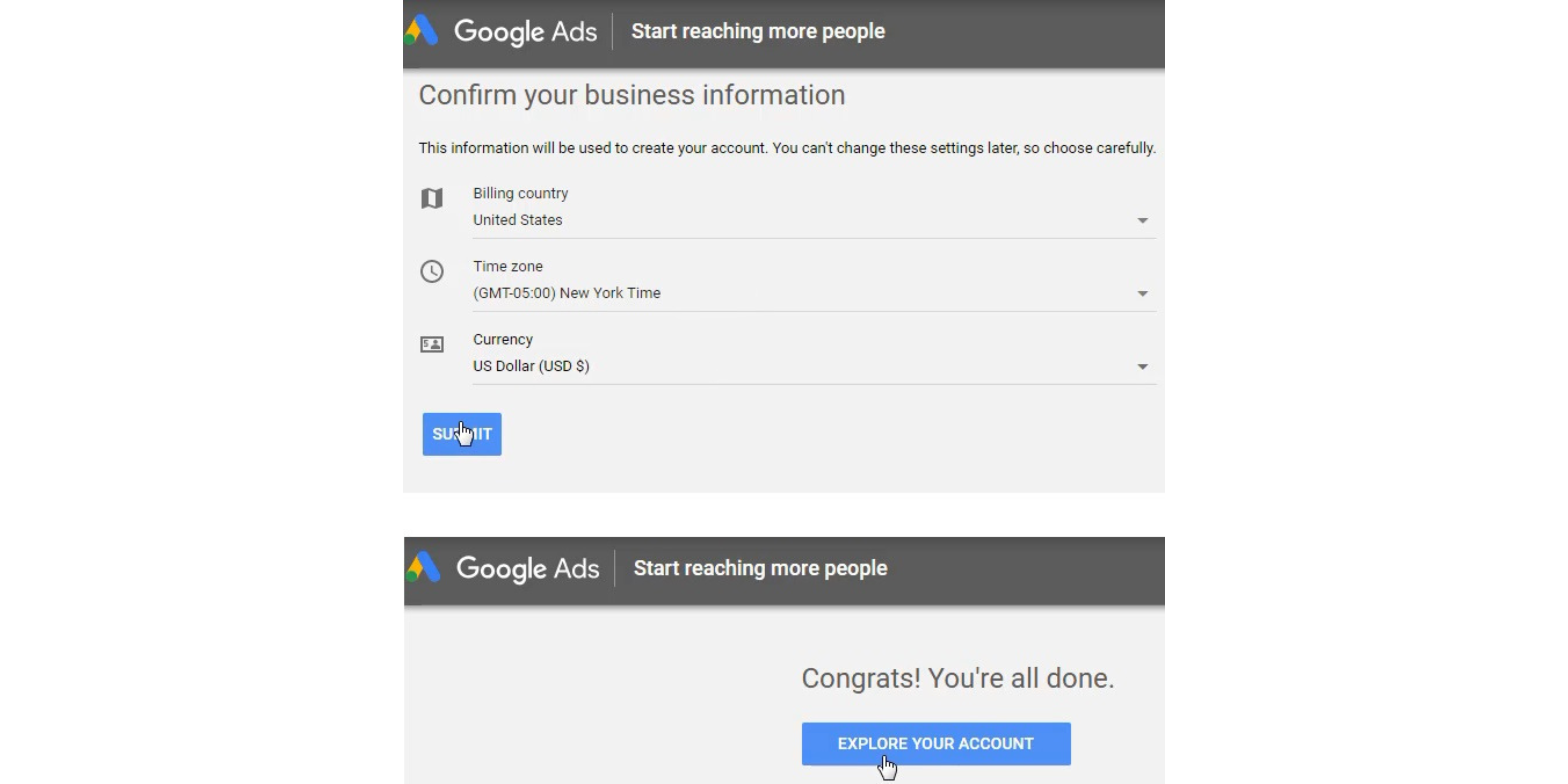
You may have to confirm a few settings before you launch your account. After this step, you will be almost ready to get started with your first campaign. Ultimately, you need to create your account and ensure you are using the full version of Google Ads to get access to all the features.
Step 5 – view Google Ads Account Overview
- Your account overview and campaign overview screen should look like the screen below.

Next, I will show you how to set up conversion tracking and your first campaign. If you are using Google Ads for the first time, there is a lot to learn about using the interface. The more you work in your account, the easier it will become.
Step 6 – Link Your Google Ads and Google Analytics Accounts
- Create a Google Analytics account and Link your AdWords and Analytics accounts together. We’ll start in Google Analytics and then confirm the link in our Ads account.
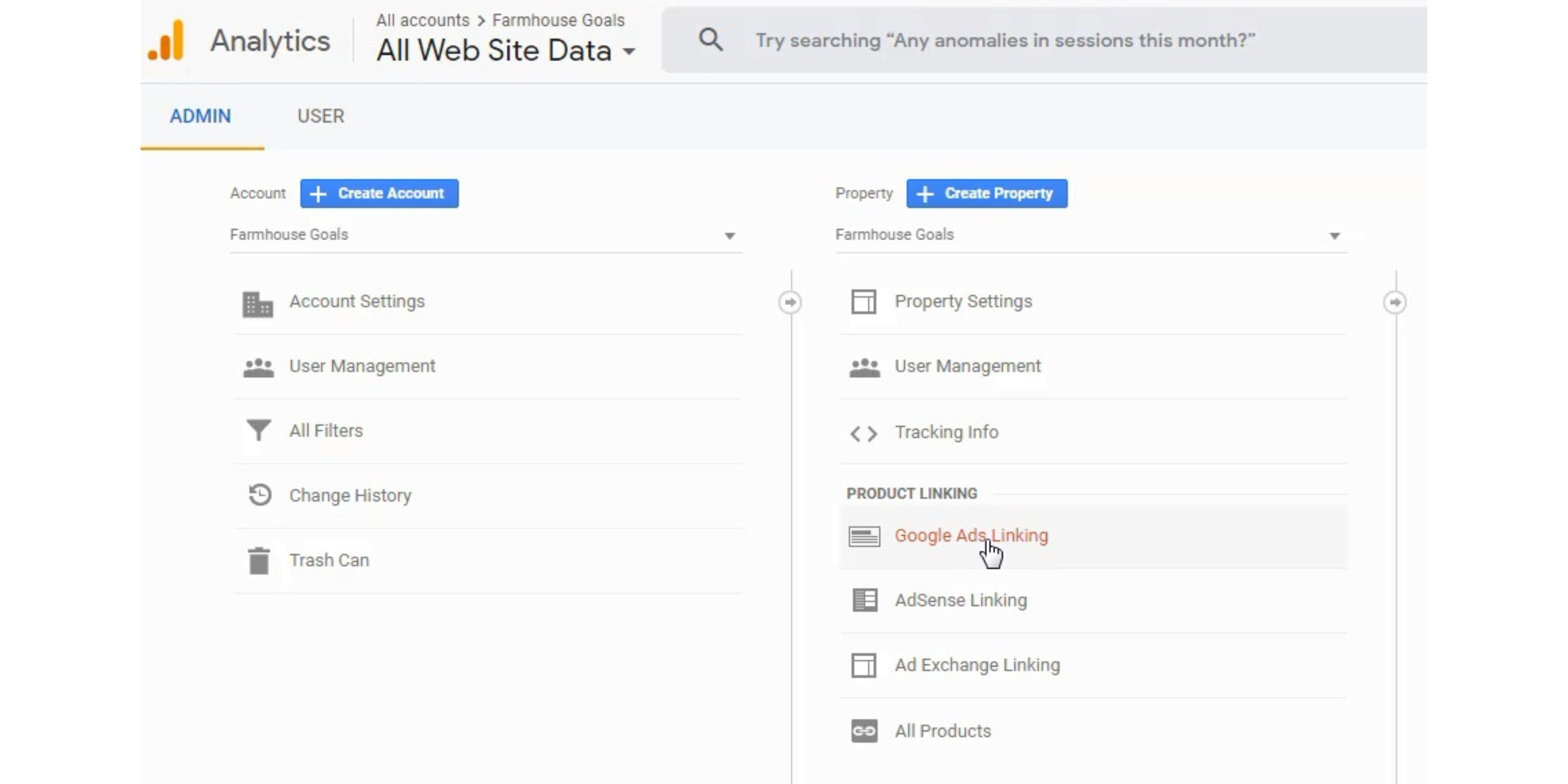
Configure the linking and confirm it through your Google Analytics Account.
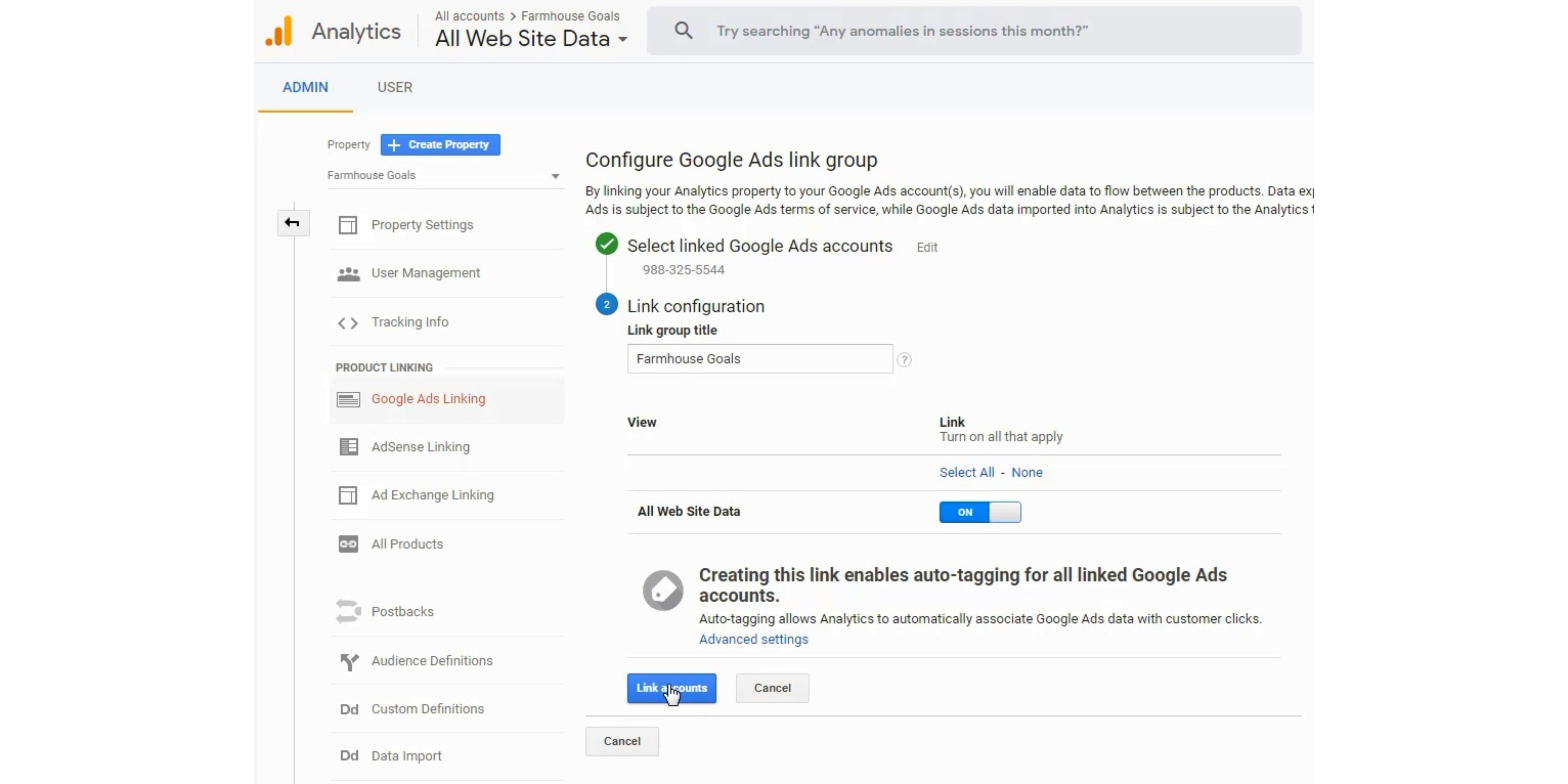
When you sign in to your Google Analytics account, you want to go to the Admin screen and click on the ‘Google Ads Linking’ URL. You can go through that URL to make sure you connected your 2 accounts. Next, you will confirm the link through the Tools menu in your Google Ads Account.
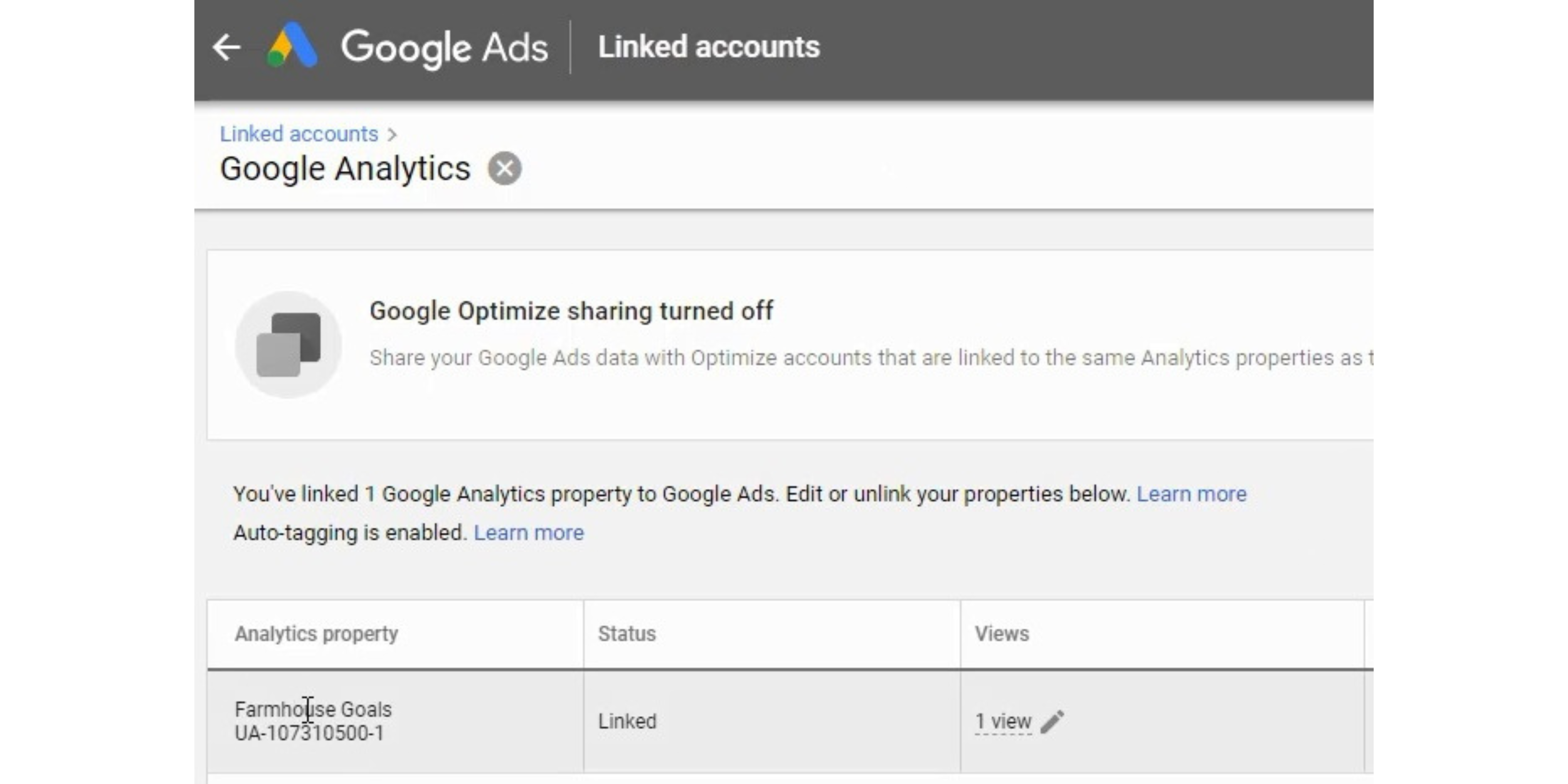
Step 6 is much easier when you are using the same Google account for your Analytics and Ads accounts. Essentially, you need to the accounts to be able to communicate so you can set up conversion tracking and track your campaigns. You should see ‘Linked’ under status on that page and Auto-Tagging should be enabled as well.
Step 7 – Set – Up Google Ads Conversion Tracking
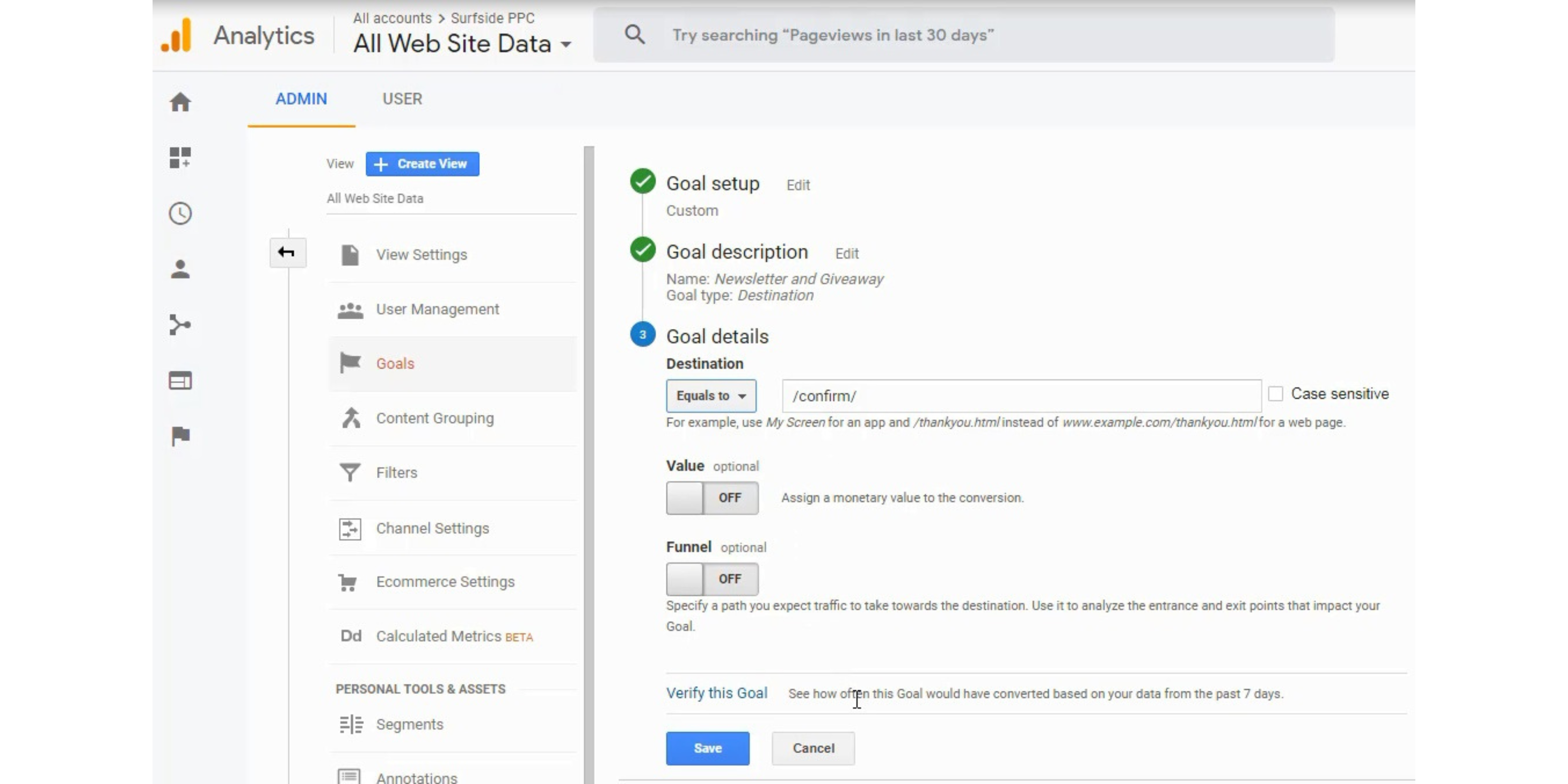
- Create Goals in Google Analytics or Enable C-commerce reporting in Google Analytics. Then, import conversions into your Google Ads Account.
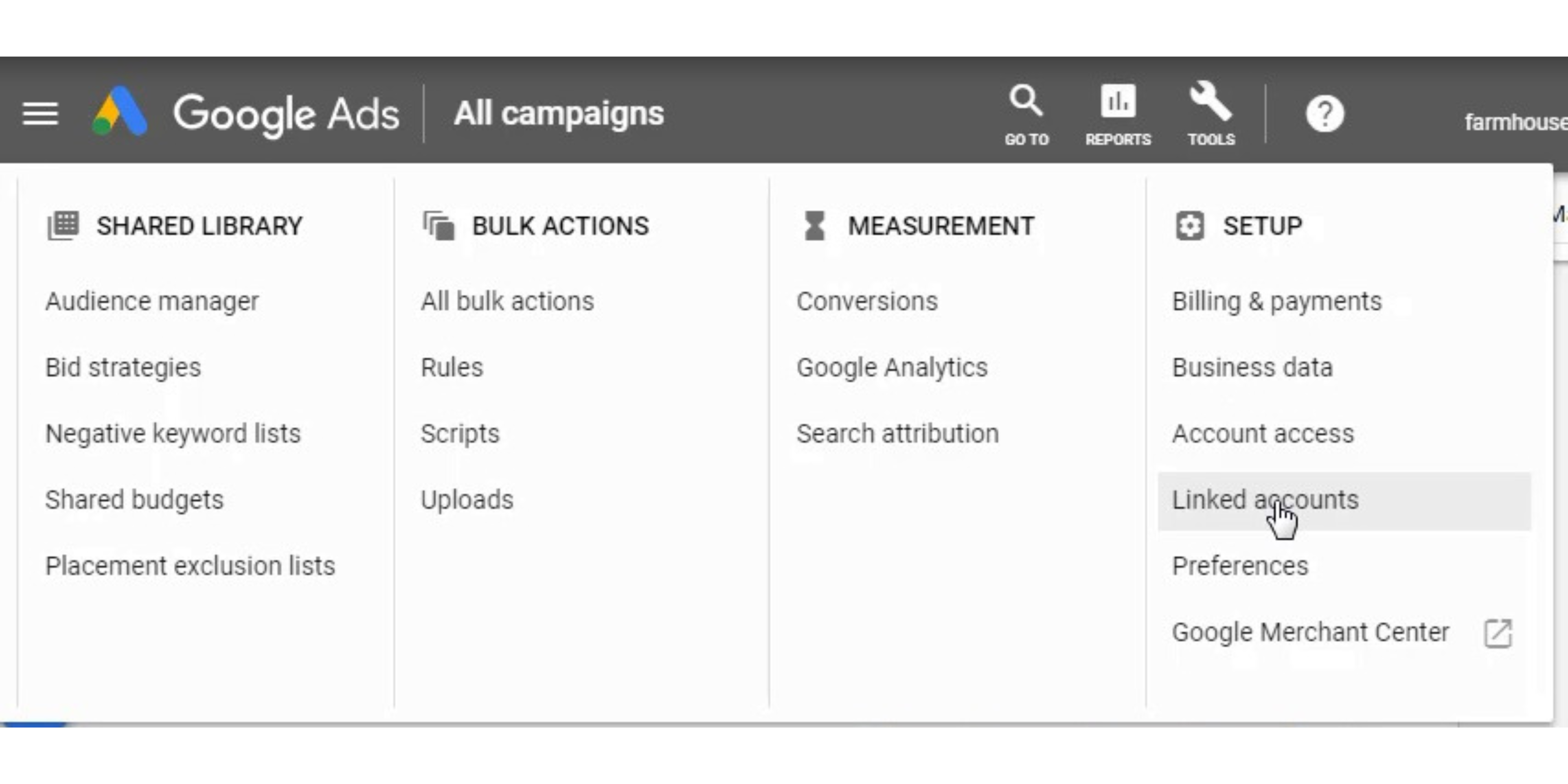
Now that you have created Google Analytics Goals, you want to go back to Google Ads, click on the Tools menu, and click on the ‘Conversions’ link from the dropdown menu.
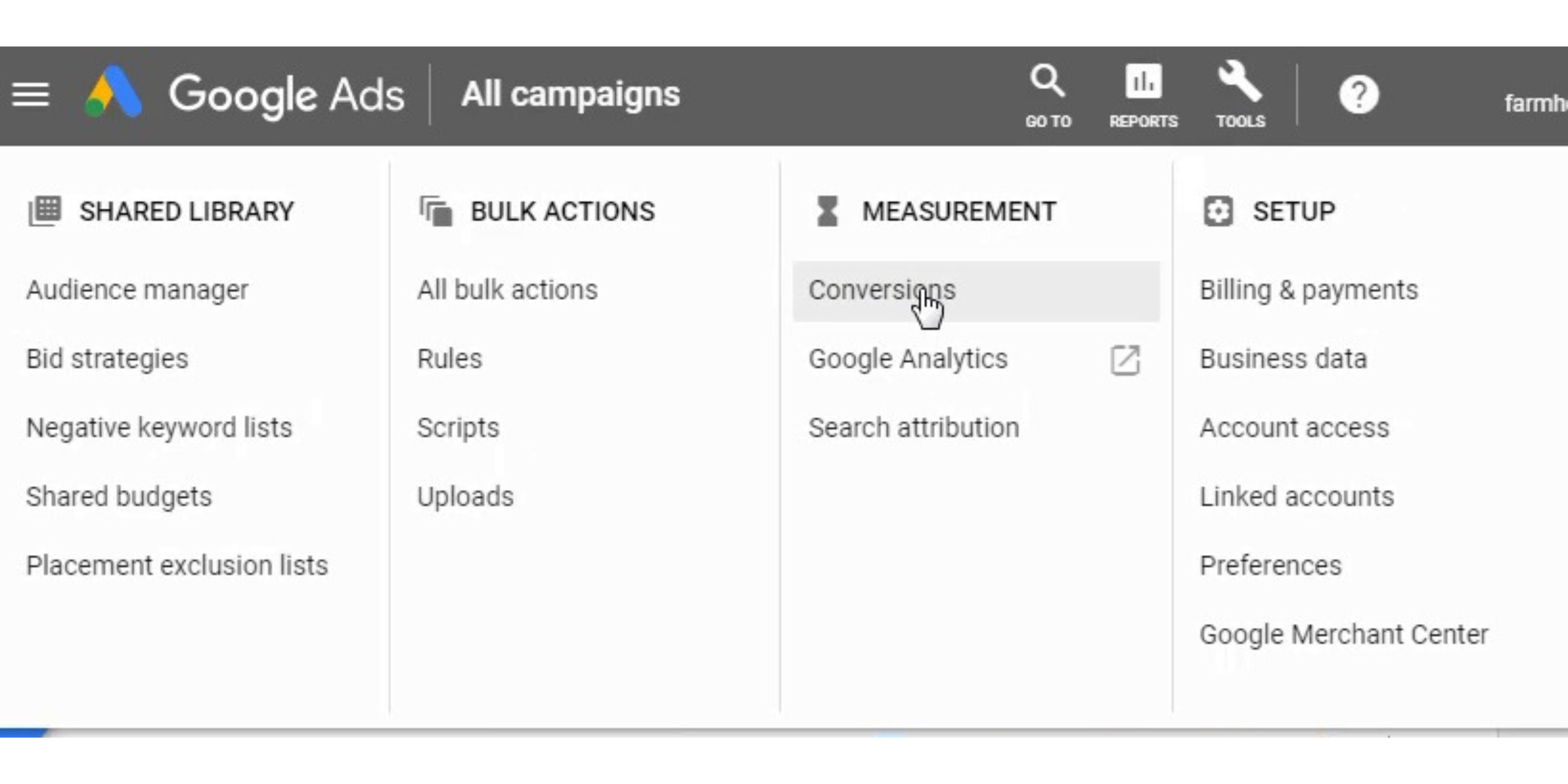
Confirm the link by going to the Tools menu, clicking on Linked Accounts, clicking on Google Analytics, and making sure the link is completely set up and Auto-Tagging is enabled.
Next, you want to import a new conversion action. You will click on the plus-sign from the main Conversions screen in Google Ads to add the key conversions you want to optimize your campaigns for. Generally, that would include driving leads, sales, or both.
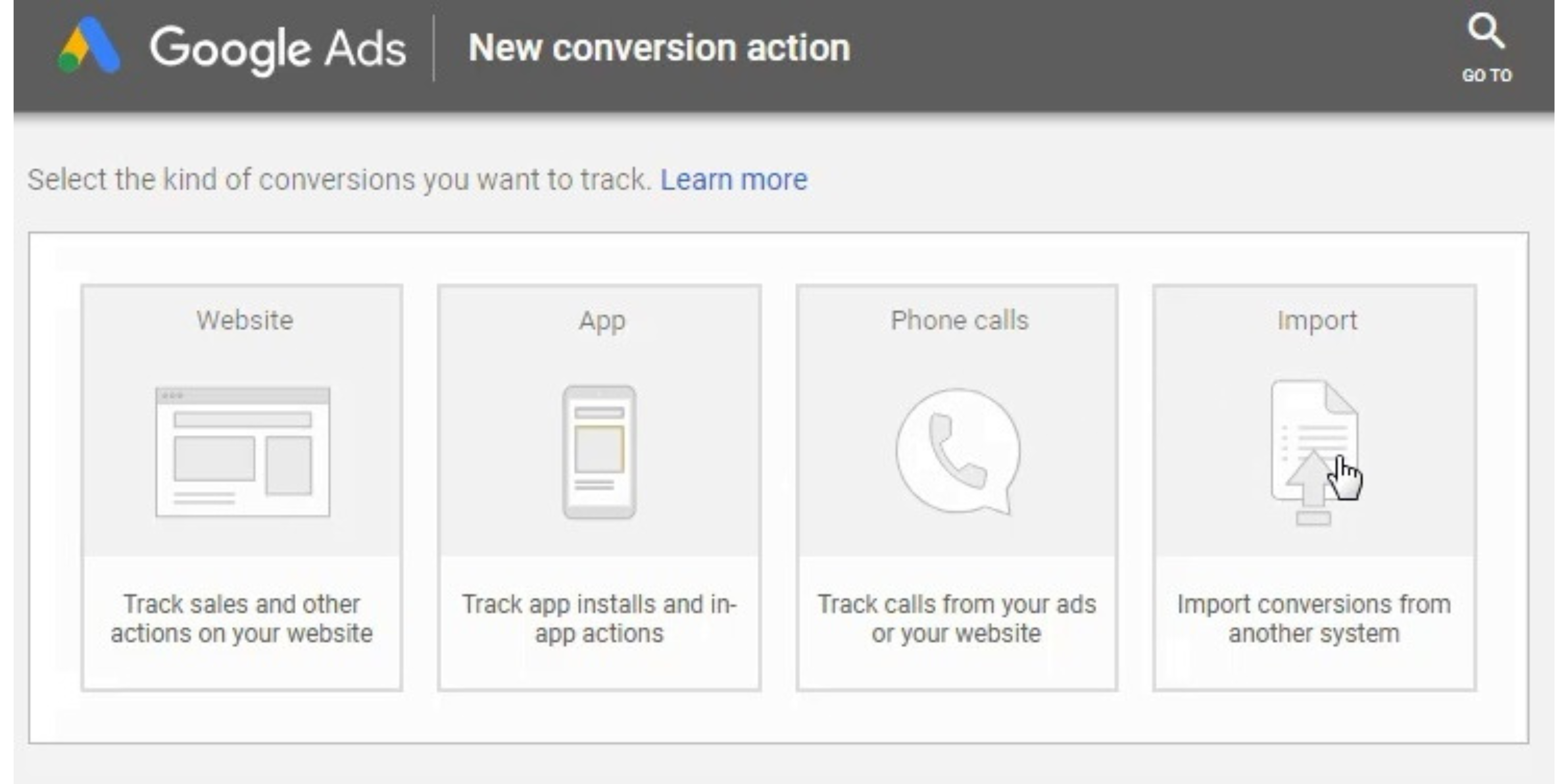
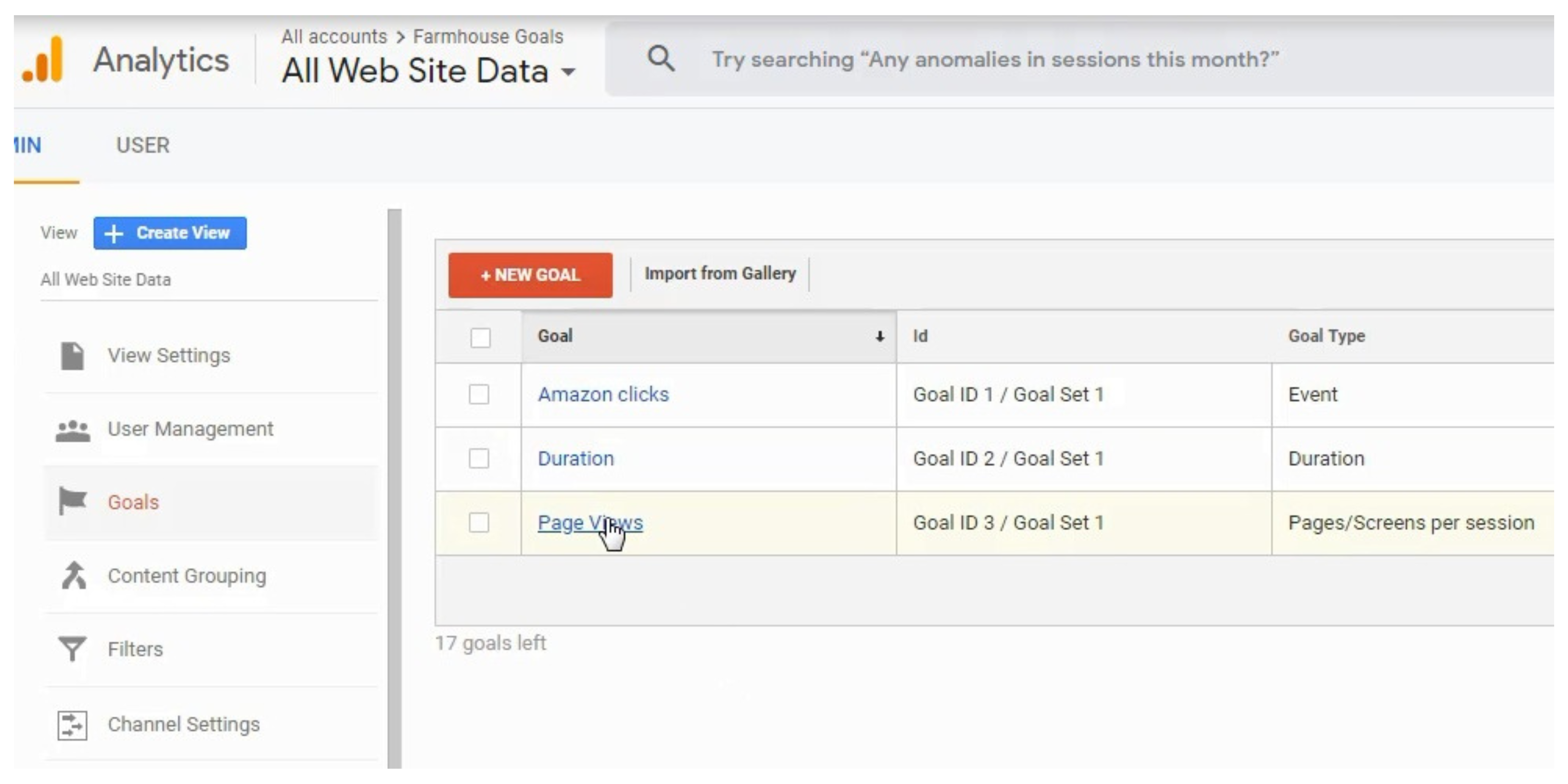
Choose to import conversions from Google Analytics.
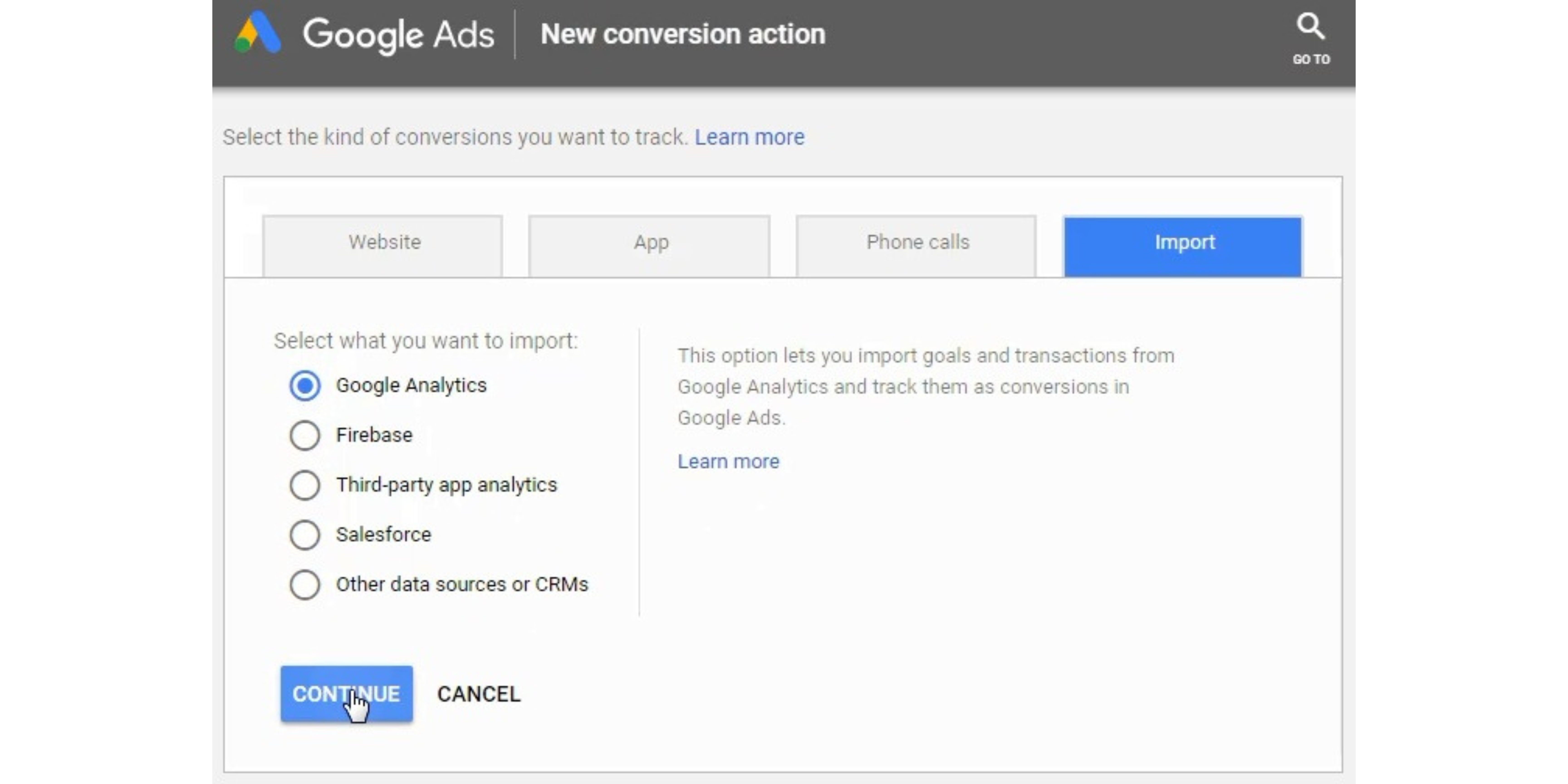
Choose the conversions you want to import. The Goals you have created can be imported now. You can import a Smart Goal, a Transaction, or you can import Lead actions.

You can watch the conversion tracking video below to learn more about importing conversions into your Google Ads account. There are different ways to track conversions and the video will give you more insight.
Step – 8 Conversion Action Settings
Update conversion action setting to categorize a conversion, set a value for a conversion, and decide whether you want to include the conversion in your conversions column for your campaign.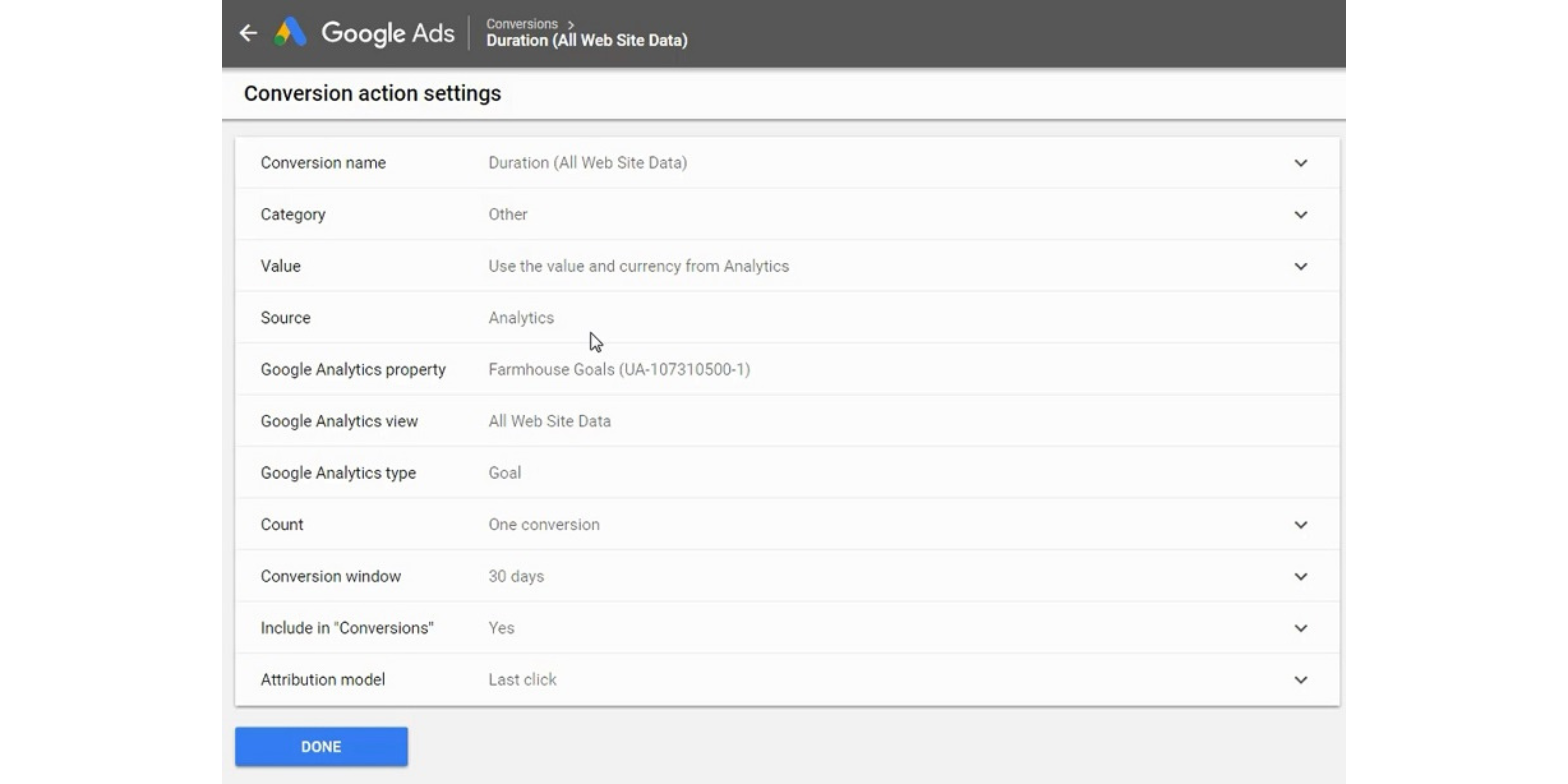
You can set a conversion value or use the conversion from Google Analytics. That will allow you to track your Return On Ad Spend directly in Google Ads account. For example, if you sell a product for $50, you can set that value for each conversion.
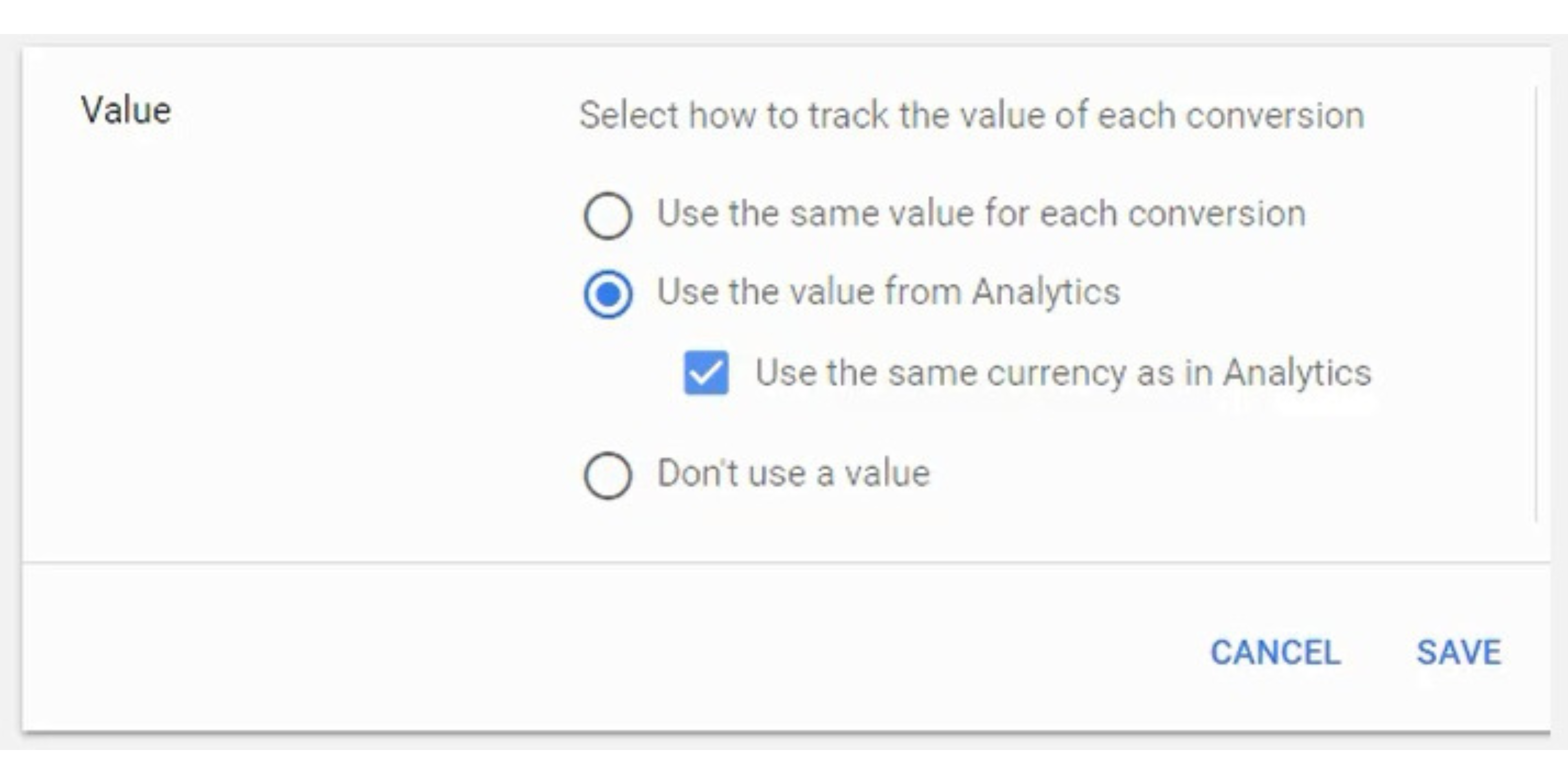
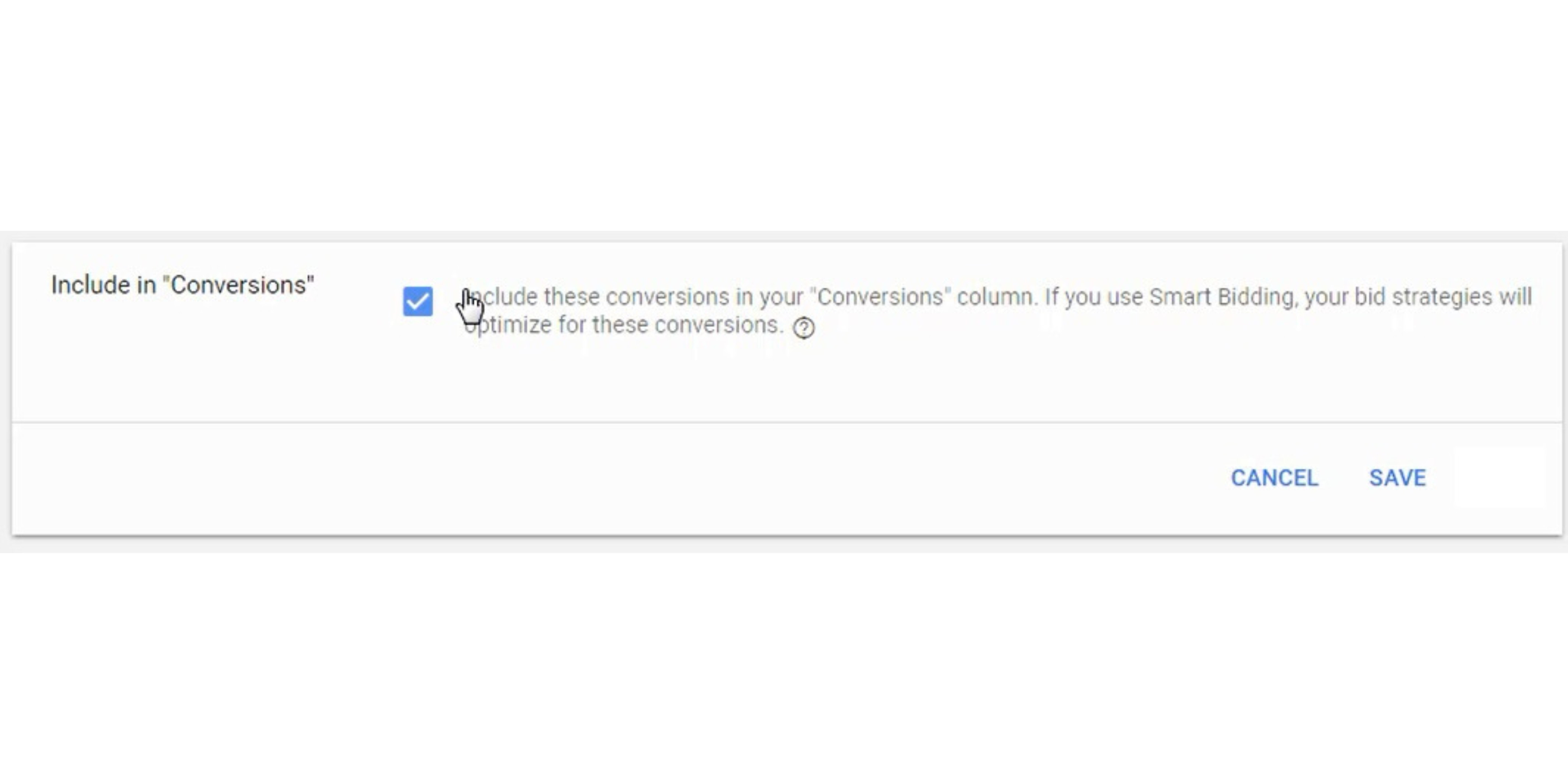
Next, you want to make sure that you include the conversion in your conversions column. There are some cases where you want to import a conversion and don’t want to include it.
Step – 9 Attribution Modeling
Choose an attribution model for your conversion. Since people may have multiple interactions with your business before reaching a conversion, you want to pick the best attribution model for your business.
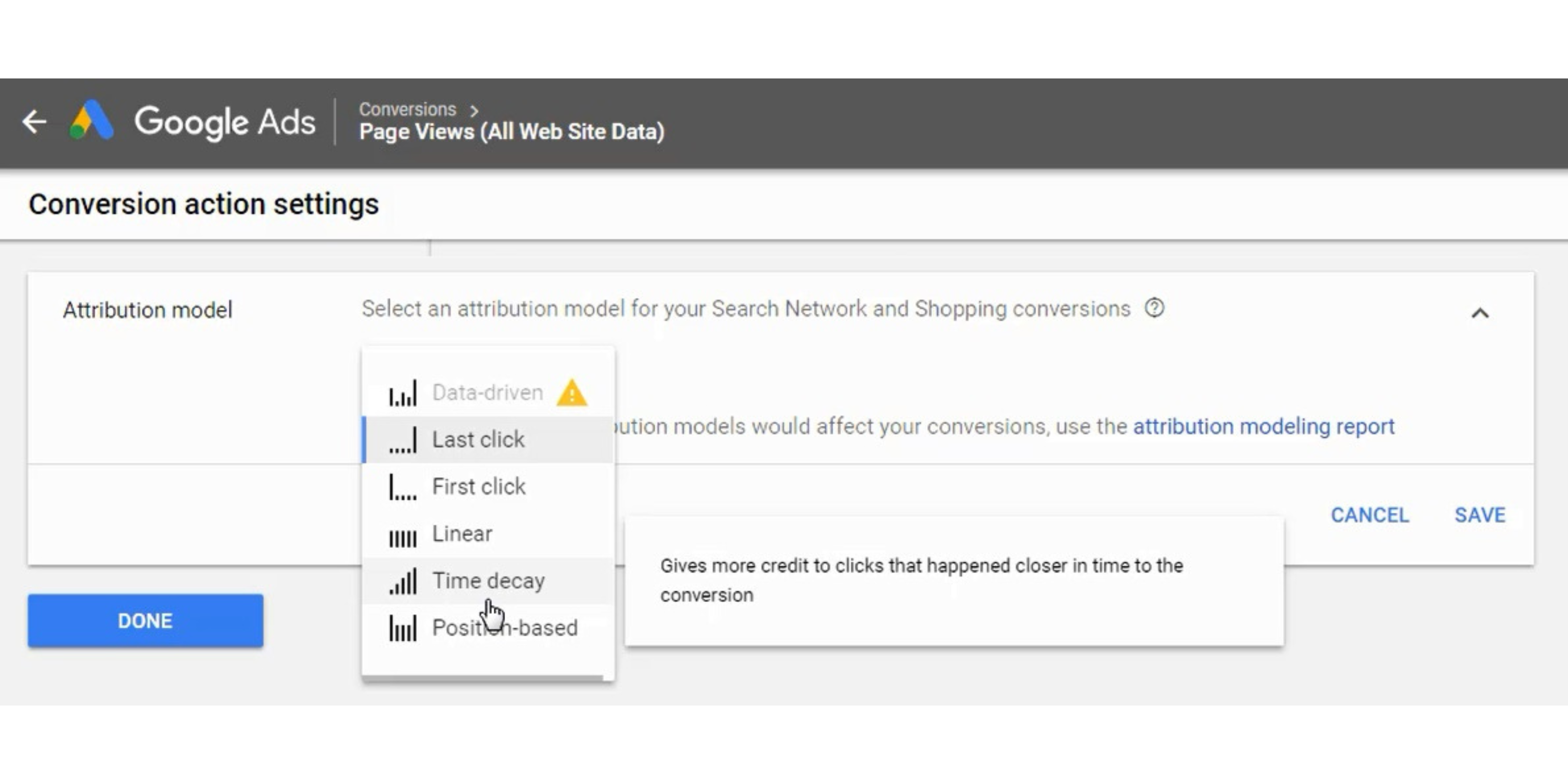
There are 6 different attribution models at this time. The 6 models are data-driven, last click, first click, linear, time decay, and position based. You can watch the video below for more information about the different models you can choose for your search network and shopping conversions.
Step 10 – Create a Campaign
You can click on the plus-sign (+) to create a campaign in Google Ads. Then you will be able to choose your campaign type and your objective.
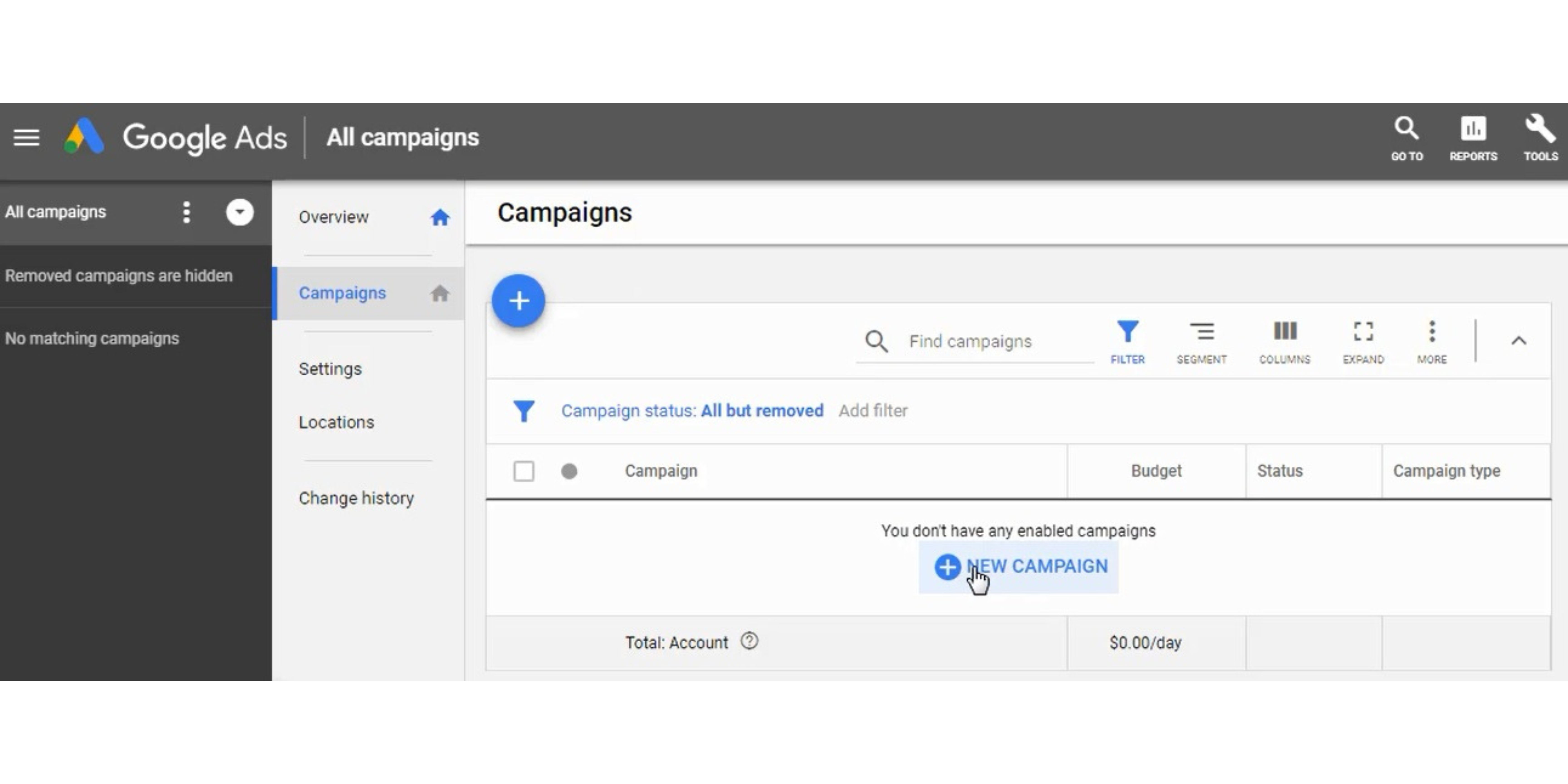
Once you create your campaign, you need to select your campaign type, and for this example will be creating a search campaign. You can also choose Display, Video, App, and Shopping campaigns at this point as well.

Step 11 – Choose Google Network, Targeting, and Audiences
Choose the network you will be targeting. For search campaigns, you should only target the Search Network and Search Partners. For Display campaigns, choose the Google Display Network. In addition, set your location targeting, language targeting, and audiences.
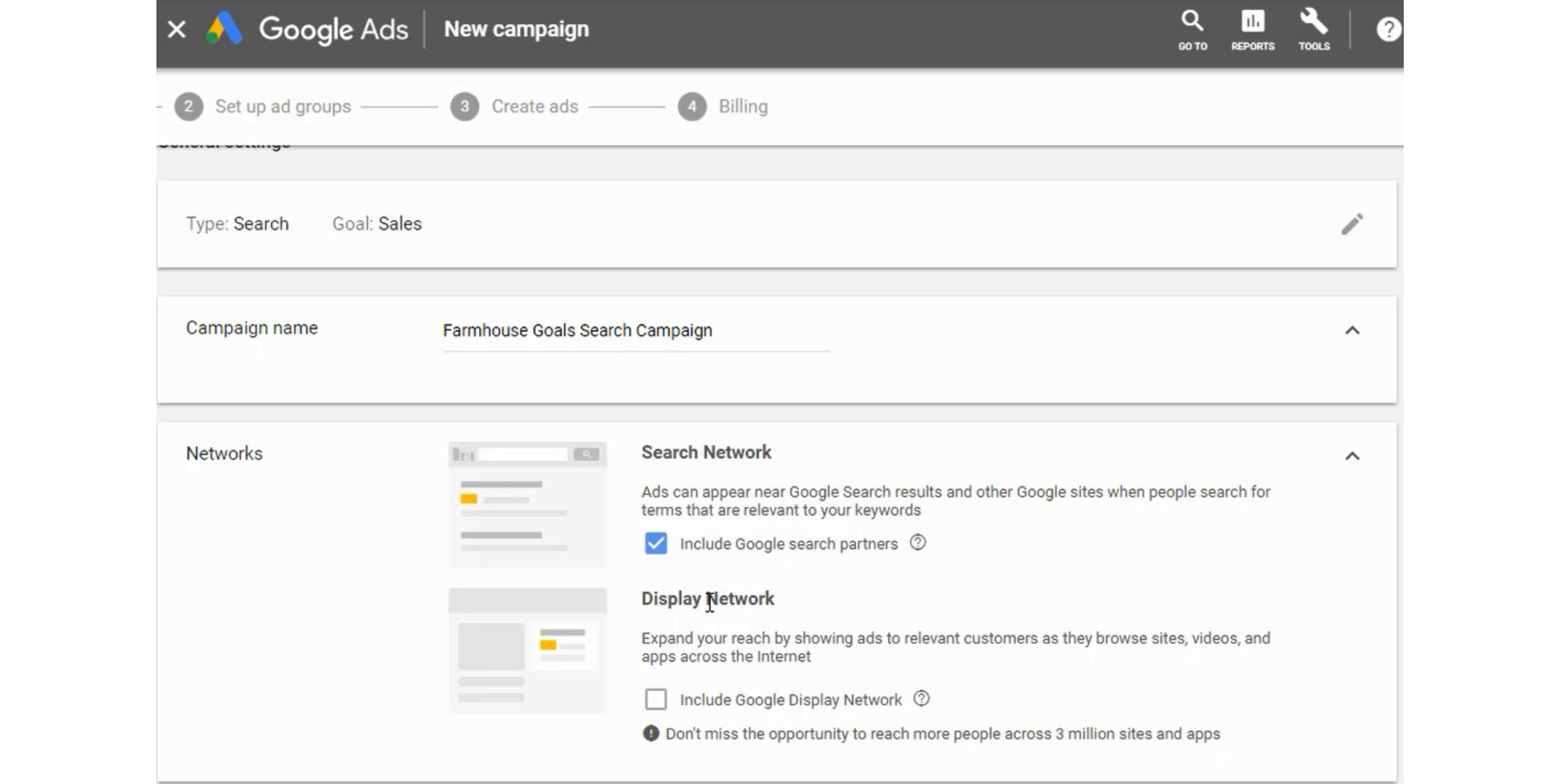
After you name your campaign and choose your network, you want to choose the locations you will target and the languages your customers speak. In addition, you can add audiences to your campaign as well.
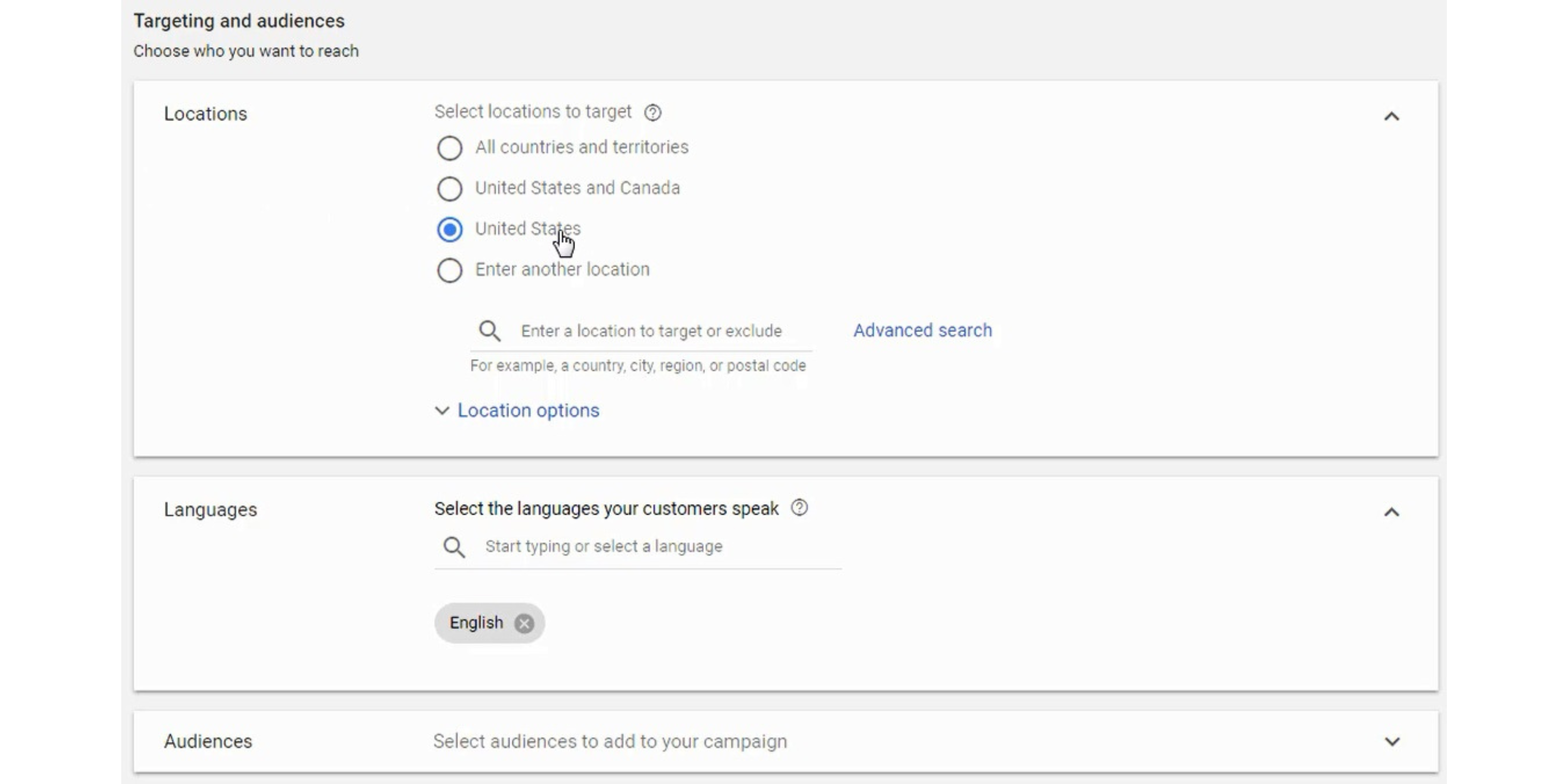
Step 12 – Set Your Budget and Bid Strategy
Choose your daily budget and your bid strategy for your campaign. You should consider using a smart bidding strategy like Enhance CPC, Target CPA, or Target ROAS.
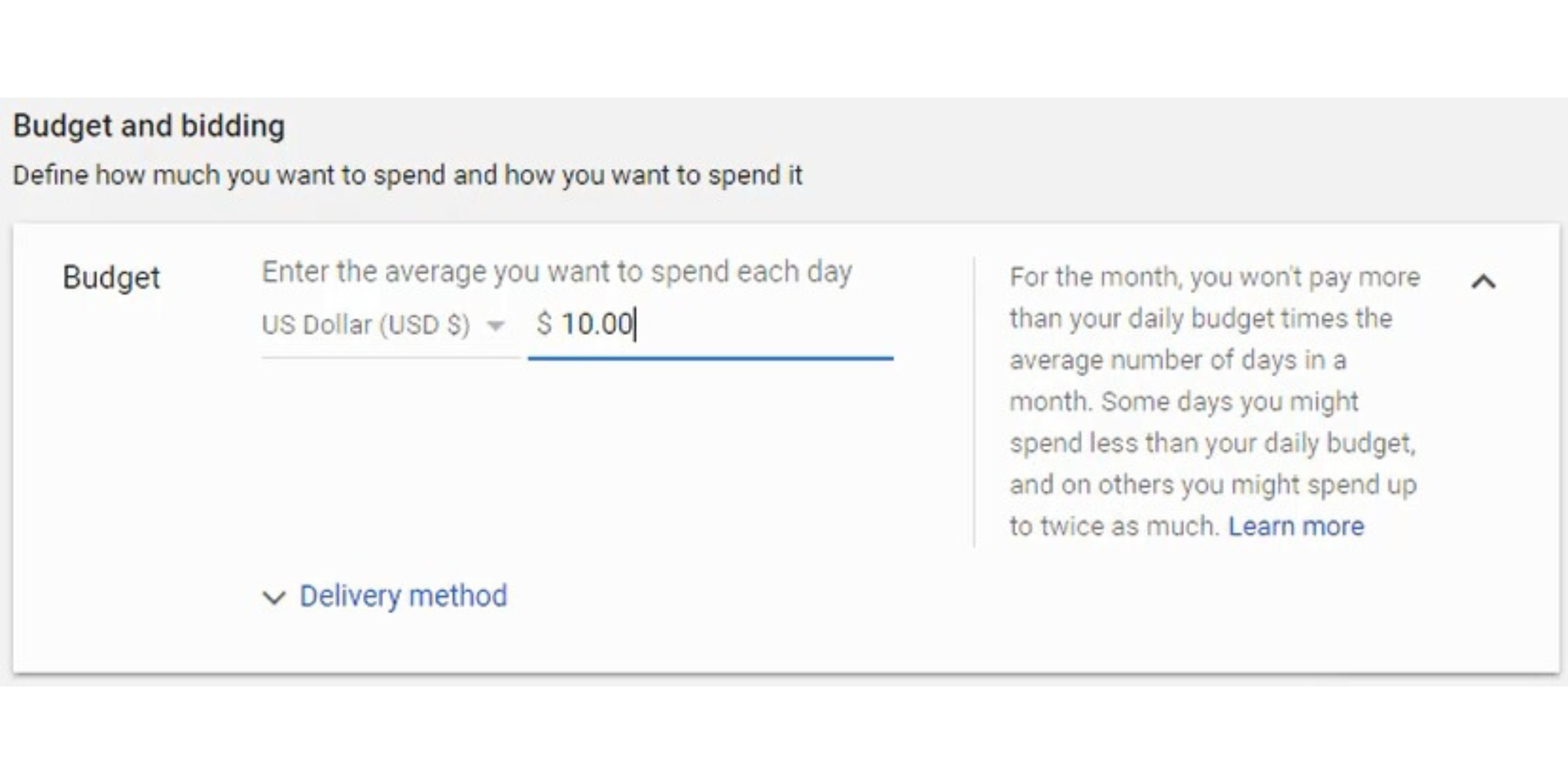
There is a video below that describes how I currently approach my bid strategy through Google Ads. It can be difficult to find the best bidding strategy for new campaigns, but you want to use Target CPA or Target ROAS once you start driving conversions.
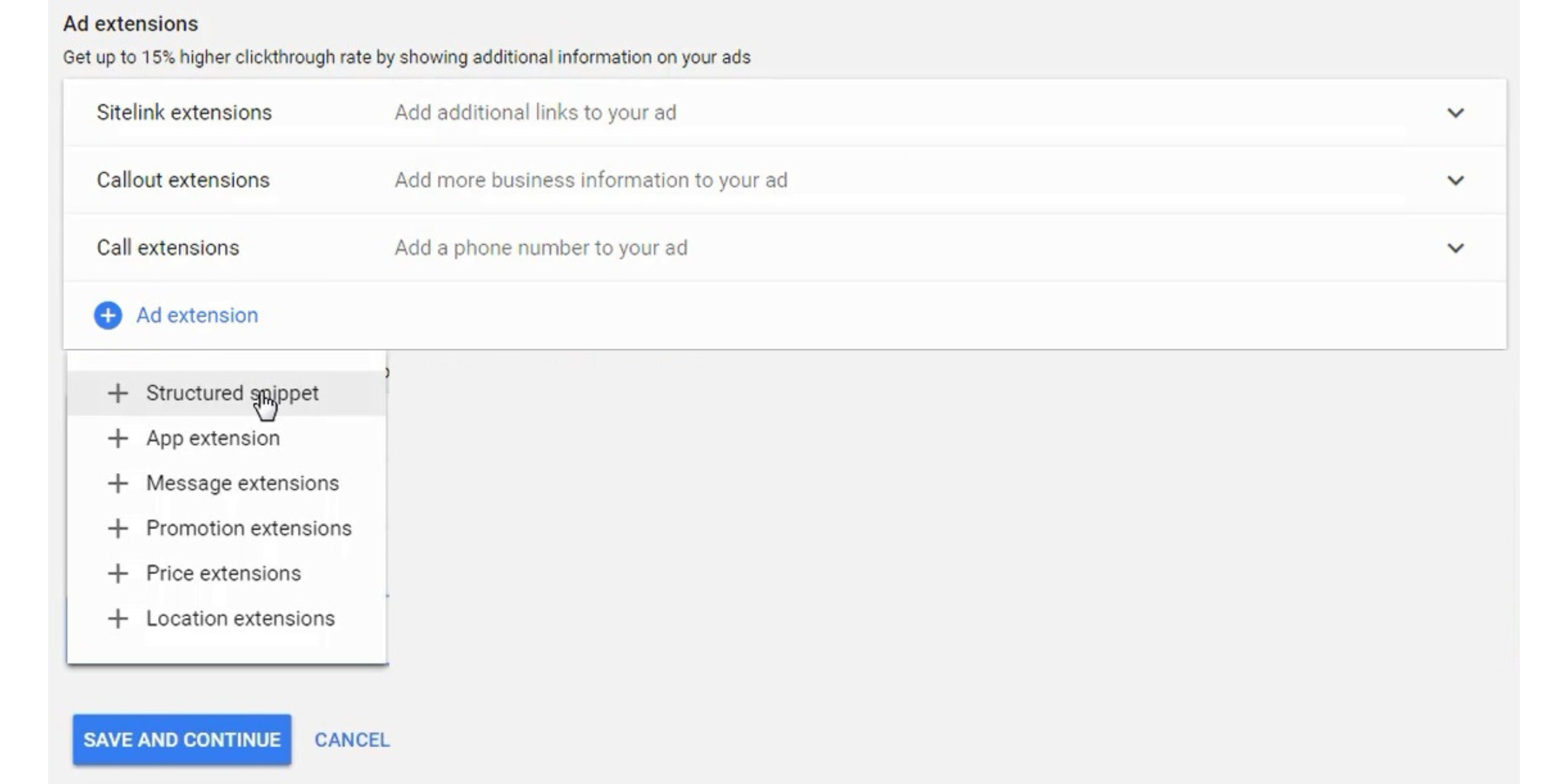
Step 13 – Create Google Ads Ad Extensions
Use all relevant Ad Extensions for your advertisements. Make sure you go through the Ad Extensions one-by-one apply every one that applies to your business.
Step 14 – Set-Up Your Ad Groups by Theme
Your Ad Groups should be grouped together so that you can target relevant keywords that send traffic to targeted landing pages.

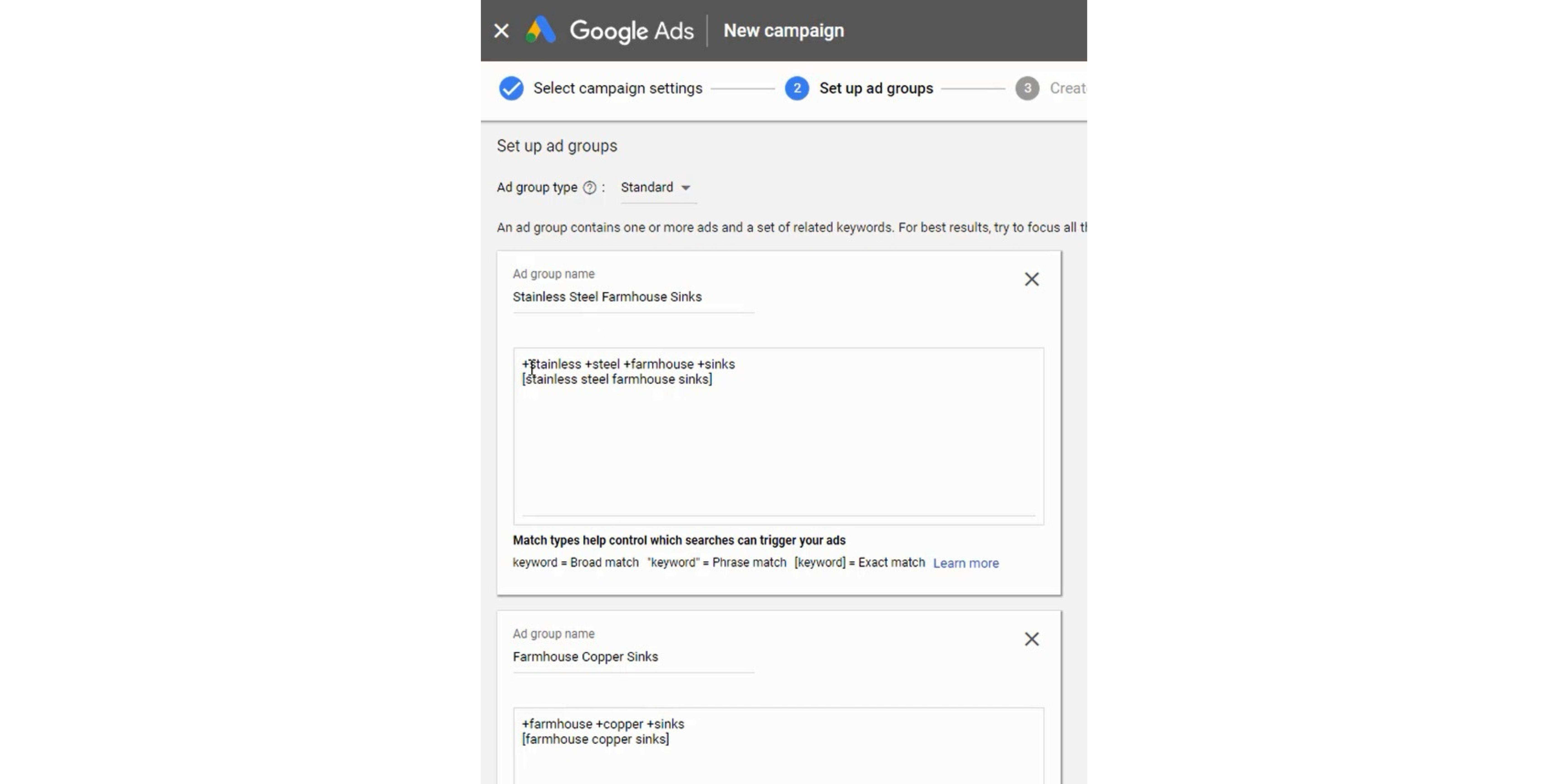
Step 15 – Target Keywords in Your Ad Group
Target keywords in your Ad Groups. I recommend using broad match modifier and/or exact match keywords. You should avoid broad match keywords altogether.
Step 16 – Create Your Google Ads to Match Keywords in Ad Group
Your ads should match closely to the keywords in your Ad Groups. Keywords, ads, and landing pages should align very closely.
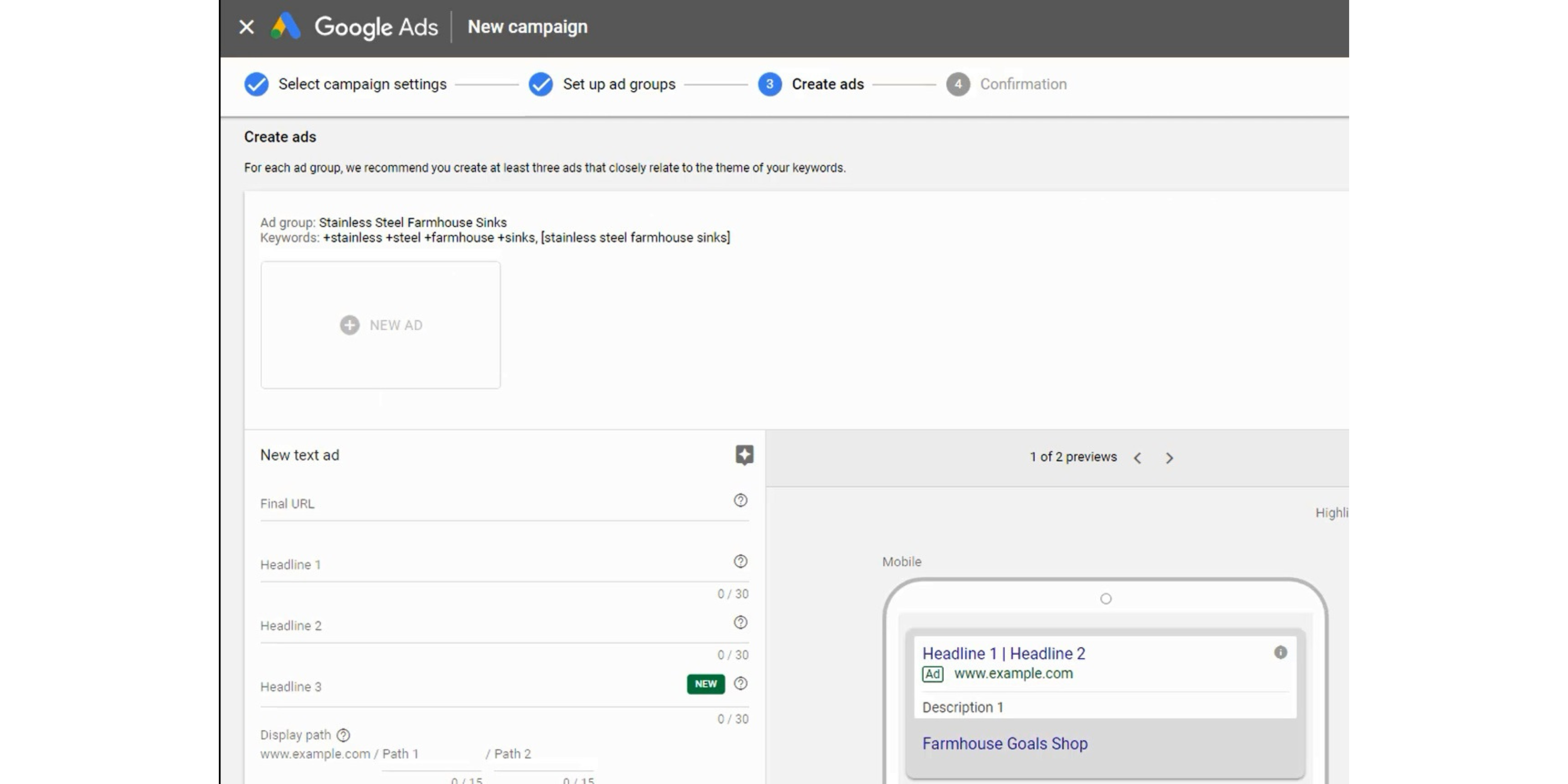
Step 17 – Create Ads, Set Headlines, and Set Final URLs
Your need to fill out all of the fields for your advertisements. You want to set Final URLs that match your keywords, create great headlines, and write descriptions that will clearly show the benefits of your products and services.
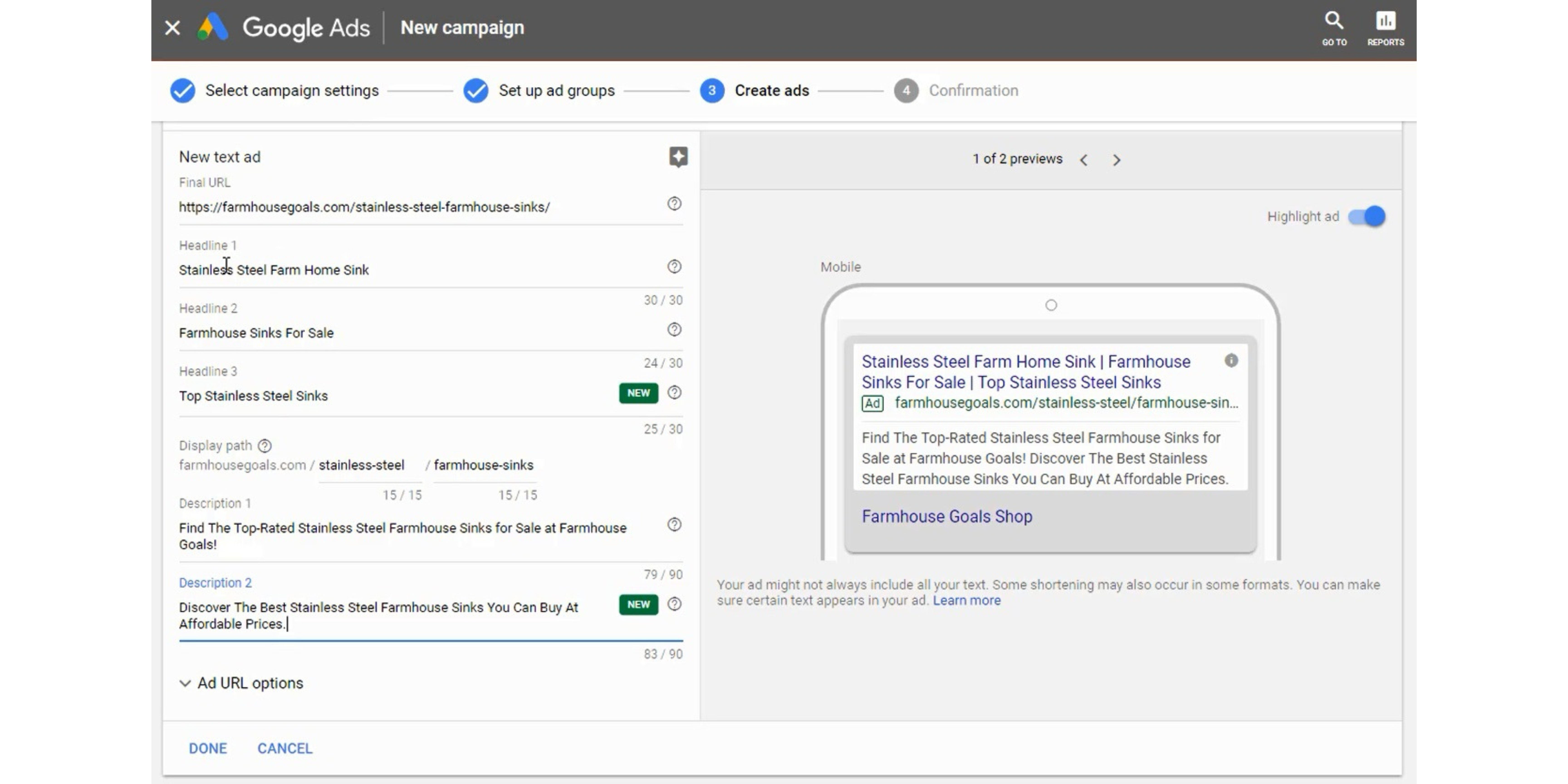
Step 18 – Create 2-3 Text Ads Per Ad Group
It is a best practice in Google Ads to create multiple ads in each ad group. You should create at least 1 Responsive Search Ad and at least 1 Expanded Text Ad in each Ad Group.
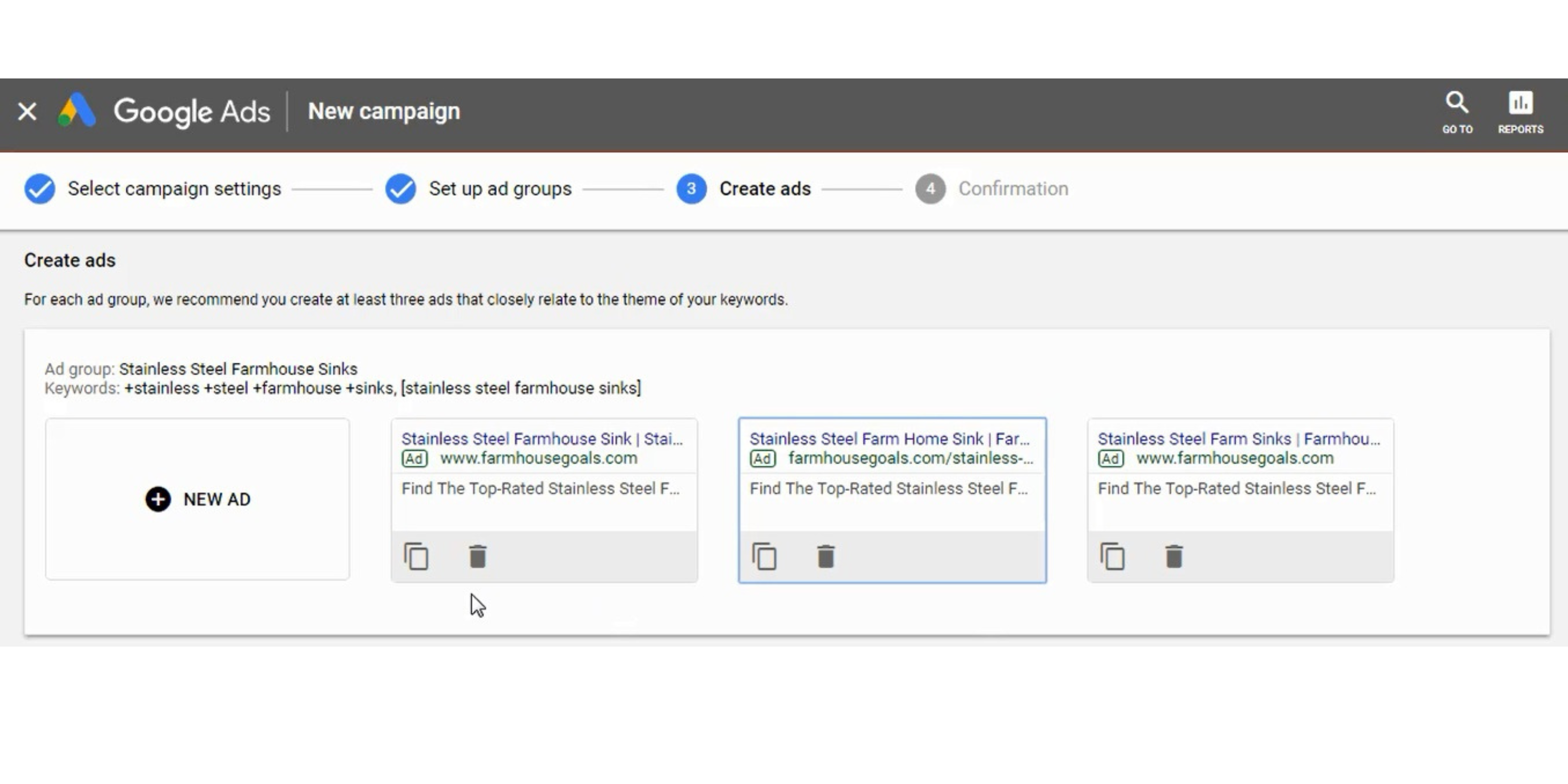
Step 19 – Launch Your Google Ads Campaign
Click Save and Continue to launch your Google Ads campaign. Then click to Continue to Campaign to view your search campaign in your account.
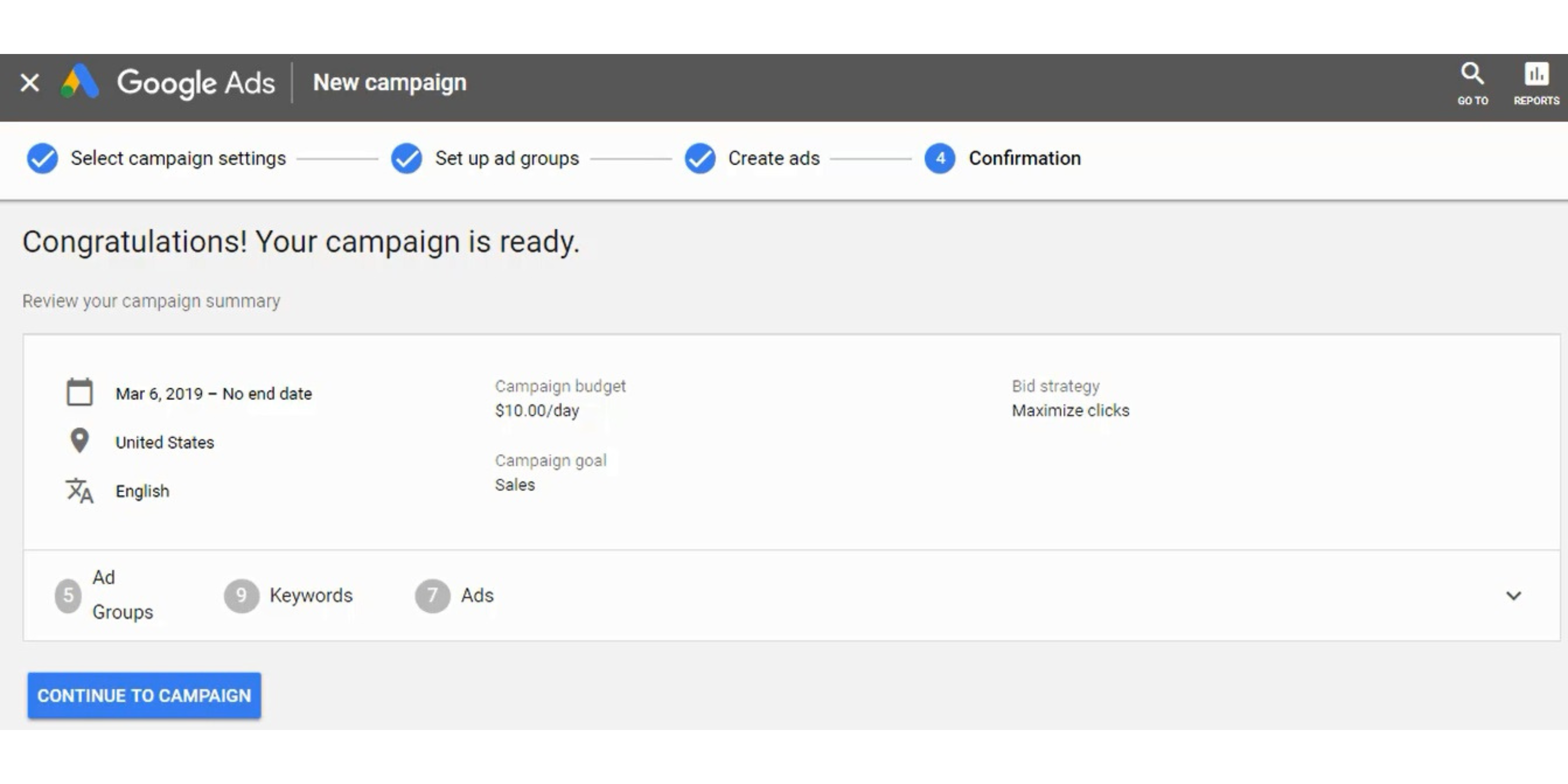
Your campaign will begin running after you go through approvals. You still need to optimize your Google Ads campaigns to drive conversions for your business.
End of Google Ads Tutorial
Frequently Asked Questions
Google AdWords, now called Google Ads, is an online advertising platform provided by Google. It allows businesses to create and display ads on Google’s search engine results pages (SERPs), as well as on other Google partner websites and platforms.
Google Ads operates on a pay-per-click (PPC) model, where advertisers bid on keywords relevant to their products or services. When a user enters a search query that matches the advertiser’s chosen keywords, the ad may appear on the SERPs. Advertisers pay only when someone clicks on their ads.
Using Google Ads offers several benefits, including:
- Targeted reach: Ads can be targeted based on keywords, demographics, locations, and more.
- Cost control: Advertisers have control over their budgets and bidding strategies.
- Measurable results: Google Ads provides detailed analytics to track ad performance and measure ROI.
- Ad format variety: Various ad formats are available, including search ads, display ads, video ads, shopping ads, and more.
- Remarketing opportunities: Advertisers can reach users who have previously interacted with their website or shown interest in their products.
The cost of Google Ads varies depending on factors such as your budget, bidding strategy, competitiveness of keywords, and quality score. Advertisers can set a daily budget and adjust bids as needed. Google Ads operates on an auction system, where advertisers compete for ad placements based on their bids and relevance.
To create effective ads on Google Ads, consider the following tips:
- Conduct keyword research to target relevant and high-performing keywords.
- Create compelling ad copy that clearly communicates your value proposition.
- Use ad extensions to provide additional information and improve ad visibility.
- Optimize landing pages to ensure a seamless user experience.
- Regularly monitor and analyze ad performance to make data-driven optimizations.
Google Ads provides robust tracking and reporting features. You can track metrics such as clicks, impressions, conversions, click-through rates (CTRs), and cost per conversion. Additionally, you can set up conversion tracking to measure specific actions users take on your website, such as purchases or form submissions.
Remember that Google Ads is a dynamic platform, and staying updated with its features, best practices, and industry trends can help you achieve optimal results.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Google AdWords, now known as Google Ads, is a powerful advertising platform that can help businesses reach their target audience, drive website traffic, and increase conversions. When used effectively, it can be a valuable tool for businesses of all sizes to promote their products or services.
It’s important to note that achieving success with Google Ads requires ongoing monitoring, analysis, and optimization. Regularly reviewing your campaign performance and making necessary adjustments will help you maximize the benefits and ensure a higher ROI.
In summary, Google Ads offers businesses an effective way to reach their target audience, increase brand visibility, and drive conversions. By leveraging its features and following best practices, businesses can create successful ad campaigns that deliver measurable results and contribute to their overall marketing objectives.
