Introduction
Data collection is the process of gathering and analyzing information from various sources to gain valuable insights that can be utilized in digital marketing strategies. In the digital age, the evolution of data collection has transformed the way businesses understand consumer behavior and make informed decisions. This article explores the role of data in digital marketing, different data collection techniques, privacy and ethical considerations, benefits, limitations, and challenges associated with data collection.
The Role of Data in Digital Marketing
A. Understanding Data Collection

1. Distinguishing between structured and unstructured data
- Structured data refers to information that is organized and easily accessible, such as customer demographics or transaction records.
- Unstructured data encompasses less organized information, like social media posts or customer feedback, which requires advanced analysis techniques.
2. Importance of real-time data for digital marketing
- Real-time data allows marketers to make immediate adjustments and respond to market trends.
- Timely insights obtained from real-time data enable businesses to create targeted and relevant marketing campaigns.
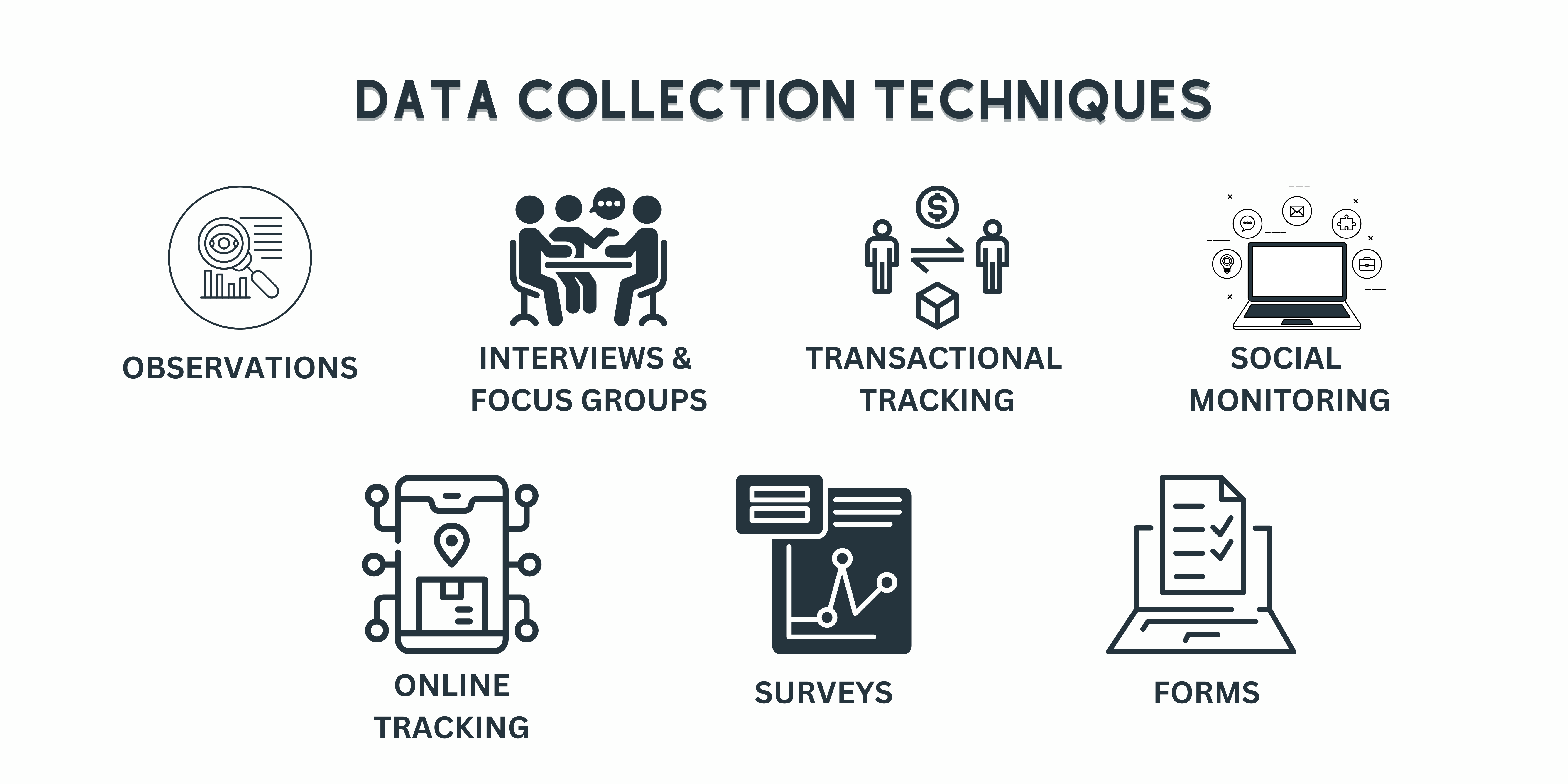
3. Overview of data collection techniques
- Data collection techniques vary and can include tracking user behavior, implementing surveys and feedback systems, monitoring social media, and collecting mobile data.
B. Leveraging Data in Marketing Strategies
1. Personalization and targeted campaigns
- By analyzing customer data, businesses can personalize marketing messages and create targeted campaigns that resonate with individual preferences, increasing engagement and conversion rates.
2. Improved customer segmentation through data analysis
- Data analysis enables businesses to segment their audience more effectively, tailoring marketing efforts to specific demographics or customer segments for better results.
3. Enhancing customer experience through data-driven marketing
- Utilizing data, businesses can gain insights into customer preferences and behavior, allowing for the creation of personalized experiences, improving customer satisfaction, and fostering long-term relationships.
Data Collection Techniques
A. Tracking User Behavior
1. Web analytics and cookies
- Web analytics tools track website visitors’ behavior, providing valuable insights into page views, click-through rates, and user journey analysis.
- Cookies, small text files stored on users’ devices, enable marketers to track user preferences and provide a personalized web experience.
2. Heatmaps and clickstream data
- Heatmaps visually represent user activity on a website, highlighting areas of interest and identifying potential usability issues.
- Clickstream data analysis tracks users’ click paths, allowing marketers to understand navigation patterns and optimize website layout and design.
3. Tracking pixels and conversion tracking
- Tracking pixels embedded in websites or emails help monitor specific user actions, such as purchases or newsletter sign-ups, providing data for conversion rate analysis.
- Conversion tracking measures the effectiveness of marketing campaigns by tracking user activities from click to conversion, helping businesses optimize their strategies.
B. Surveys and Feedback
1. Implementing online surveys
- Online surveys allow businesses to collect specific information directly from customers, such as their preferences, satisfaction levels, or buying habits.
- Survey responses provide valuable insights for improving product offerings, customer experience, or identifying new market trends.
2. Social listening and sentiment analysis
- Businesses utilize social listening tools to monitor and analyze conversations and mentions of their brand on social media platforms.
- Sentiment analysis helps gauge customer opinions by examining the tone and emotions expressed in online conversations, providing insights for reputation management and crisis response.
3. Gathering feedback through user reviews and ratings
- User-generated reviews and ratings can be collected from platforms like Google, Yelp, or specialized industry forums, helping businesses understand customer sentiment and make informed business decisions.
C. Social Media Monitoring
1. Utilizing social media listening tools
- Social media listening tools analyze social media content, providing businesses with real-time insights into customer opinions, preferences, and trends.
- These insights are valuable for developing effective marketing strategies, identifying influential individuals, or detecting emerging trends.
2. Extracting valuable insights from social media data
- Social media data offers vast opportunities for businesses to gain actionable insights, such as customer demographics, behavior patterns, or sentiment analysis.
- By leveraging this data, businesses can refine their marketing messages, target specific audience segments, and build more meaningful connections with customers.
3. Understanding the power of viral content
- Viral content has the potential to reach a vast audience, generating significant exposure and brand awareness.
- Monitoring social media data helps identify content themes or characteristics that have the potential to go viral, allowing businesses to capitalize on these opportunities and maximize their marketing impact.
D. Mobile Data Collection
1. Geolocation data and its impact on marketing
- Geolocation data obtained from mobile devices provides valuable insights into customer movement patterns and preferences, enabling businesses to deliver location-based marketing messages and offers.
- By targeting customers with relevant and contextually appropriate content, businesses can increase engagement and conversion rates.
2. App usage analytics and in-app surveys
- Analyzing app usage data allows businesses to understand customer behaviors within their mobile apps, identifying areas for improvement and enhancing user experience.
- In-app surveys can be implemented to gather direct feedback from users, helping businesses make data-driven decisions regarding app optimization and feature enhancements.
3. Utilizing mobile advertising data for targeting
- Mobile advertising data includes information such as device types, app usage, or browsing habits, allowing businesses to deliver targeted ads to users who are more likely to be interested in their products or services.
- By leveraging this data, businesses can optimize their mobile advertising strategies, increase click-through rates, and improve campaign ROI.
Privacy and Ethical Considerations
A. Data Protection Regulations
1. Overview of GDPR and its implications
- The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) is a data protection and privacy regulation that sets guidelines for the collection, processing, and storage of personal data of individuals within the European Union.
- Businesses operating in the EU or handling EU citizens’ data must comply with GDPR requirements, ensuring transparency and accountability in data collection and usage.
2. Ensuring compliance with data privacy laws
- Businesses must adhere to relevant data privacy laws and regulations applicable in their jurisdiction.
- Compliance includes obtaining proper consent for data collection, implementing appropriate security measures, and providing individuals with the right to access and request deletion of their personal data.
3. Safeguarding customer information and building trust
- Protecting customer information is paramount to maintaining trust and credibility.
- Employing robust data security measures, encryption techniques, and implementing strict access controls are crucial steps to safeguard customer data from unauthorized access or data breaches.
B. Ethical Data Collection Practices
1. Transparency and consent in data collection
- Businesses should clearly communicate their data collection practices to customers, including the purpose and scope of the collected data.
- Obtaining informed consent from individuals ensures transparency and mutual understanding between businesses and customers.
2. Respecting user preferences and privacy settings
- Providing users with control over their data privacy settings reinforces ethical data collection practices.
- Respecting users’ preferences, such as opting out of certain data collection activities or personalized advertising, demonstrates a commitment to privacy and builds trust with customers.
3. Handling and safeguarding sensitive customer data
- Businesses should handle sensitive customer data, such as financial information or medical records, with the utmost care and implement stringent security measures.
- Adhering to data anonymization techniques, encrypting data during transmission and storage, and limiting access to authorized personnel are essential to protect sensitive customer information.
The Benefits of Data Collection in Digital Marketing
A. Improved Market Research and Analysis
1. Extracting actionable insights from data
- Data collection allows businesses to gather in-depth information about their target market, enabling them to identify emerging trends, consumer preferences, and areas for improvement.
- These insights help make informed decisions in product development, marketing strategies, and positioning within the competitive landscape.
2. Identifying market trends and predicting consumer behavior
- Analyzing collected data helps identify market trends, anticipate consumer demands, and adapt marketing strategies accordingly.
- Predictive analytics techniques can be employed to forecast consumer behavior and make data-driven decisions that enhance competitive advantage.
3. Conducting competitor analysis through data mining
- By analyzing data related to competitor strategies, pricing, promotions, or customer sentiment, businesses can gain a competitive edge.
- Data mining techniques assist in extracting valuable insights that guide decision-making regarding market positioning, pricing strategies, and product differentiation.
B. Enhanced Targeting and Conversion Rates
1. Personalized advertising and retargeting
- Data collection enables businesses to deliver personalized advertising campaigns tailored to individual preferences, increasing engagement and conversion rates.
- Retargeting tactics utilize collected data to display relevant ads to users who have shown previous interest in a product or service, maximizing conversion opportunities.
2. Optimizing customer acquisition and retention strategies
- Analyzing customer data helps identify high-value segments and facilitates the creation of targeted marketing tactics to acquire and retain valuable customers.
- Data-driven insights enable businesses to optimize marketing budgets, focus on the most promising customer segments, and increase customer lifetime value.
3. Harnessing predictive analytics for better conversion rates
- Leveraging predictive analytics models allows businesses to forecast customer behavior, optimize marketing efforts, and deliver personalized offers during the customer journey.
- By anticipating customer needs and tailoring marketing messages, businesses can enhance conversion rates and drive revenue growth.
C. Building Stronger Customer Relationships
1. Customized communication and messaging
- By analyzing customer data, businesses can personalize communication and messaging, ensuring relevance and resonance with individual preferences.
- Customized interactions strengthen customer relationships and foster brand loyalty.
2. Understanding customer preferences through data analysis
- Data analysis helps businesses gain a deep understanding of customer preferences, enabling the delivery of tailored experiences and offerings.
- Identifying customer desires and pain points allows businesses to meet and exceed expectations, enhancing customer satisfaction and loyalty.
3. Anticipating customer needs and delivering personalized experiences
- By utilizing data to identify patterns and trends, businesses can anticipate customer needs and offer personalized experiences, surpassing customer expectations.
- Personalization and proactive engagement build stronger customer relationships and increase customer lifetime value.
Limitations and Challenges of Data Collection
A. Data Quality and Accuracy
1. Ensuring data integrity and reliability
- Data quality and accuracy are essential for making informed decisions and actions.
- Regular data cleansing, validation, and maintaining data integrity standards help minimize errors and improve the reliability of collected data.
2. Dealing with incomplete or inaccurate data
- Incomplete or inaccurate data can lead to misinterpretation and ineffective decision-making.
- Implementing data validation techniques, cross-referencing multiple data sources, and using statistical methods can help mitigate these challenges.
3. Overcoming biases and misinterpretation of data
- Human biases and misinterpretation of collected data can lead to flawed insights and decision-making.
- Implementing data analysis methods that account for bias, such as statistical techniques or involving diverse perspectives, helps ensure more accurate and reliable results.
B. Data Security Risks
1. Protecting data from cyber threats and breaches
- Data breaches can result in significant financial losses, reputational damage, and legal consequences.
- Implementing robust cybersecurity measures, such as encryption, access controls, and regular security audits, helps mitigate the risks associated with cyber threats.
2. Developing robust data security measures
- Businesses should establish security protocols and procedures to protect collected data from unauthorized access or data leaks.
- Encryption, intrusion detection systems, data anonymization techniques, and regular security audits contribute to robust data security practices.
3. Addressing data governance and compliance issues
- Complying with data governance frameworks and ensuring adherence to data protection regulations require businesses to establish clear policies and procedures.
- Regular audits, data classification, and the appointment of a data protection officer can help address data governance and compliance challenges.
C. Consumer Perception and Trust Issues
1. Balancing personalization and privacy concerns
- Consumers value personalized experiences but are also concerned about privacy infringements.
- Businesses must strike a careful balance between personalization and respecting privacy rights to maintain trust and avoid negative consumer perceptions.
2. Maintaining transparent data practices to build trust
- Being transparent about data collection practices and informing customers about how their data is used fosters trust and helps alleviate concerns.
- Clearly communicating data protection measures and privacy policies builds a foundation for a trustworthy relationship with customers.
3. Addressing consumer concerns about data collection
- Businesses should actively address consumer concerns regarding data collection, privacy, and data security through proactive communication and safeguard measures.
- Offering options for data opt-out, user-friendly privacy settings, and clear consent mechanisms demonstrates a commitment to addressing consumer concerns.
Frequently Asked Questions
Data collection in digital marketing refers to the process of gathering and analyzing information from various sources, including customer behaviors, preferences, and interactions, to gain insights for optimizing marketing strategies and achieving business objectives.
Data collection helps businesses understand consumer behaviors, preferences, and market trends, enabling them to create targeted and personalized marketing campaigns that resonate with their target audience. This, in turn, improves customer engagement, conversion rates, and overall marketing effectiveness.
The risks of data collection include data breaches, cyber threats, inaccurate or incomplete data, biases, and potential damage to consumer trust. Businesses must establish robust data security measures, ensure data accuracy and reliability, and address privacy concerns to mitigate these risks.
Data protection regulations, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), set guidelines for businesses in collecting, handling, and storing personal data. Compliance with these regulations is crucial in safeguarding customer privacy, ensuring transparent data practices, and building trust with consumers.
Businesses can ensure data security by implementing robust cybersecurity measures, such as encryption, access controls, intrusion detection systems, and regular security audits. Establishing proper data governance frameworks and adhering to data protection regulations also contribute to data security.
Conclusion
Data collection plays a vital role in digital marketing strategies. By utilizing various data collection techniques such as tracking user behavior, surveys, and social media monitoring, businesses gain valuable insights into consumer preferences, behaviors, and trends. Leveraging data allows businesses to personalize marketing campaigns, enhance customer relationships, and improve targeting and conversion rates. However, businesses must also navigate privacy regulations, ensure data security, and address consumer trust concerns. Despite limitations and challenges, data collection empowers businesses to make informed decisions and drive success in the dynamic digital marketing landscape.