Introduction
As technology continues to advance at a rapid pace, virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) have emerged as two of the most exciting and innovative fields. These immersive technologies have captivated the imaginations of individuals across various industries, from gaming and entertainment to education and healthcare. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the world of VR and AR, exploring their definitions, applications, benefits, and future potential.
What is Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR)?
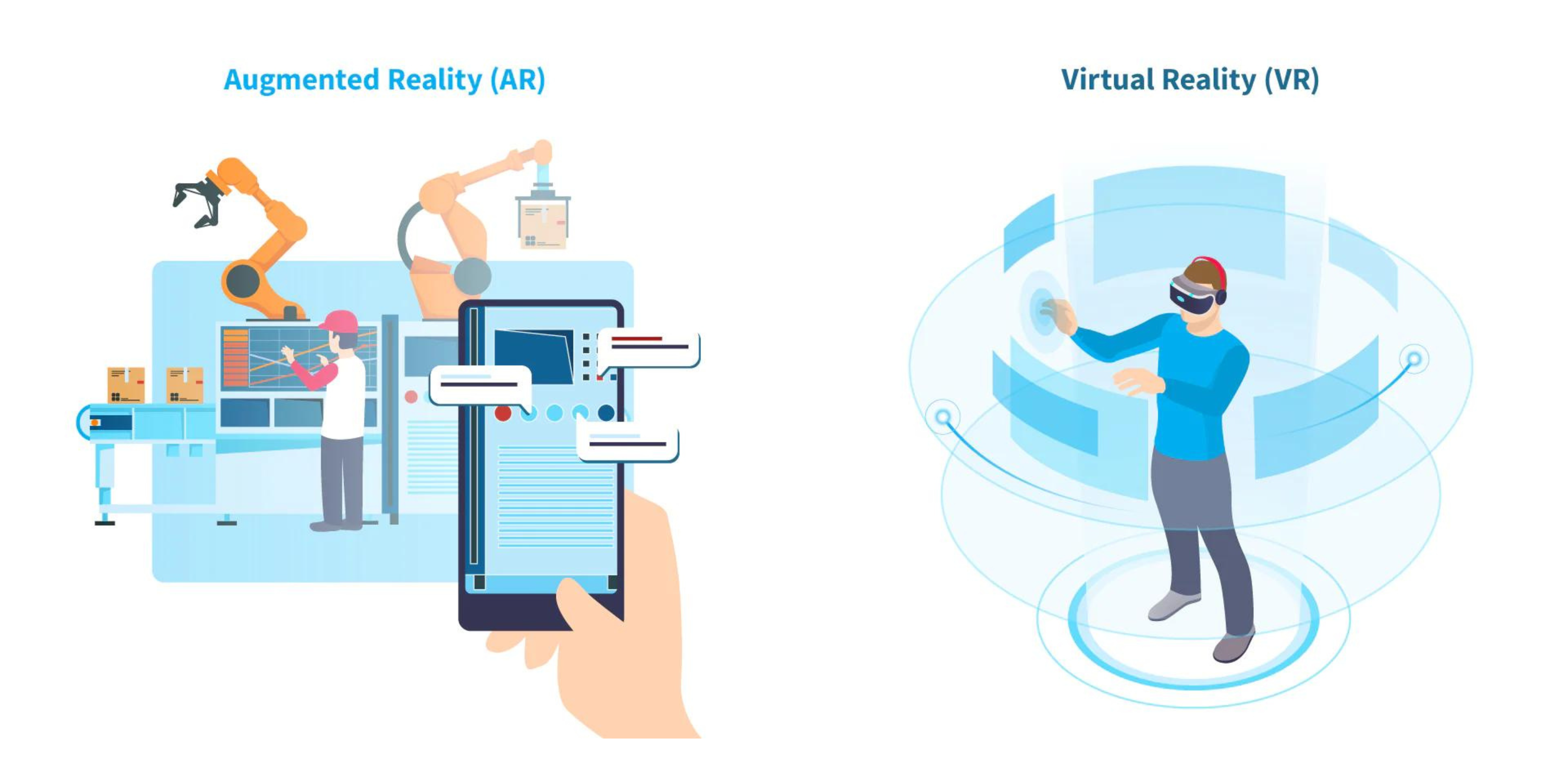
Virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) are computer-generated technologies that aim to enhance the user’s perception of reality. While both VR and AR create interactive, immersive experiences, they differ in their approach.
VR is a simulated experience that can be similar to or completely different from the real world. Through the use of advanced technology, VR transports users into a computer-generated environment where they can interact with a virtual world.
AR, on the other hand, blends the virtual and real worlds by overlaying digital information onto the user’s actual environment. With AR, users can experience an enhanced version of reality, where computer-generated elements seamlessly coexist with the physical world.
The Rise of VR and AR in Recent Years
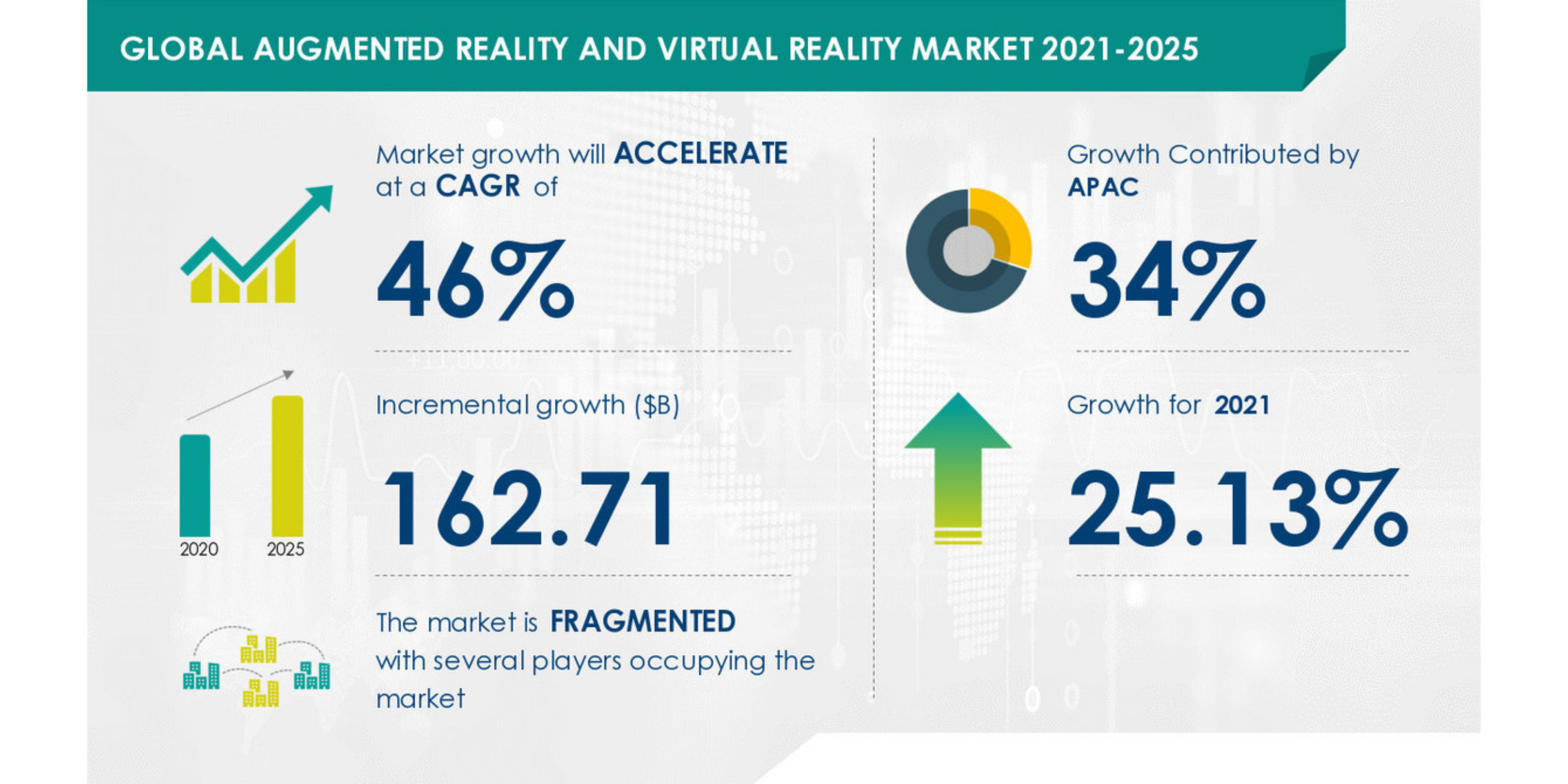
In recent years, VR and AR technologies have experienced a rapid rise in popularity and adoption. As advancements in technology make these experiences more accessible and affordable, their potential applications have multiplied.
Industries such as gaming, education, healthcare, entertainment, architecture, and retail have embraced VR and AR, harnessing their capabilities to offer unique and transformative experiences.
Exploring the Applications and Benefits of VR and AR
Understanding Virtual Reality
Definition and concept of Virtual Reality
Virtual Reality can be defined as an artificial environment that is created with the help of computer technology. It immerses users in a simulated experience where they can interact with a 3D environment.
A brief history of Virtual Reality
Virtual Reality has a long and fascinating history. It dates back to the 1960s when Morton Heilig developed the Sensorama, a machine that provided multi-sensory experiences. The following decades saw continuous advancements, leading to the development of modern VR systems.
How does Virtual Reality work?
Virtual Reality works by utilizing a combination of hardware and software components to create an immersive experience for the user. Head-mounted displays (HMDs), motion sensors, and tracking systems are used to track the user’s movements and provide a realistic sense of presence in the virtual world.
Components of a VR system
- Head-mounted displays (HMDs)
- Motion sensors
- Tracking systems
- Input devices (controllers, gloves, etc.)
- Audio systems
- Computing hardware
Immersion and sensory experiences in VR
One of the key aspects of VR is its ability to provide a high level of immersion and sensory experiences. Through visual, auditory, and sometimes haptic feedback, users can feel as though they are truly present in the virtual environment.
Types of Virtual Reality systems
- Fully immersive VR: These systems completely immerse the user in a virtual environment, blocking out the real world.
- Non-immersive VR: These systems provide a partial virtual experience while allowing users to maintain awareness of the real world.
- Augmented Virtuality (AV): This type of VR blends virtual and real elements, allowing users to interact with real-world objects in a virtual environment.
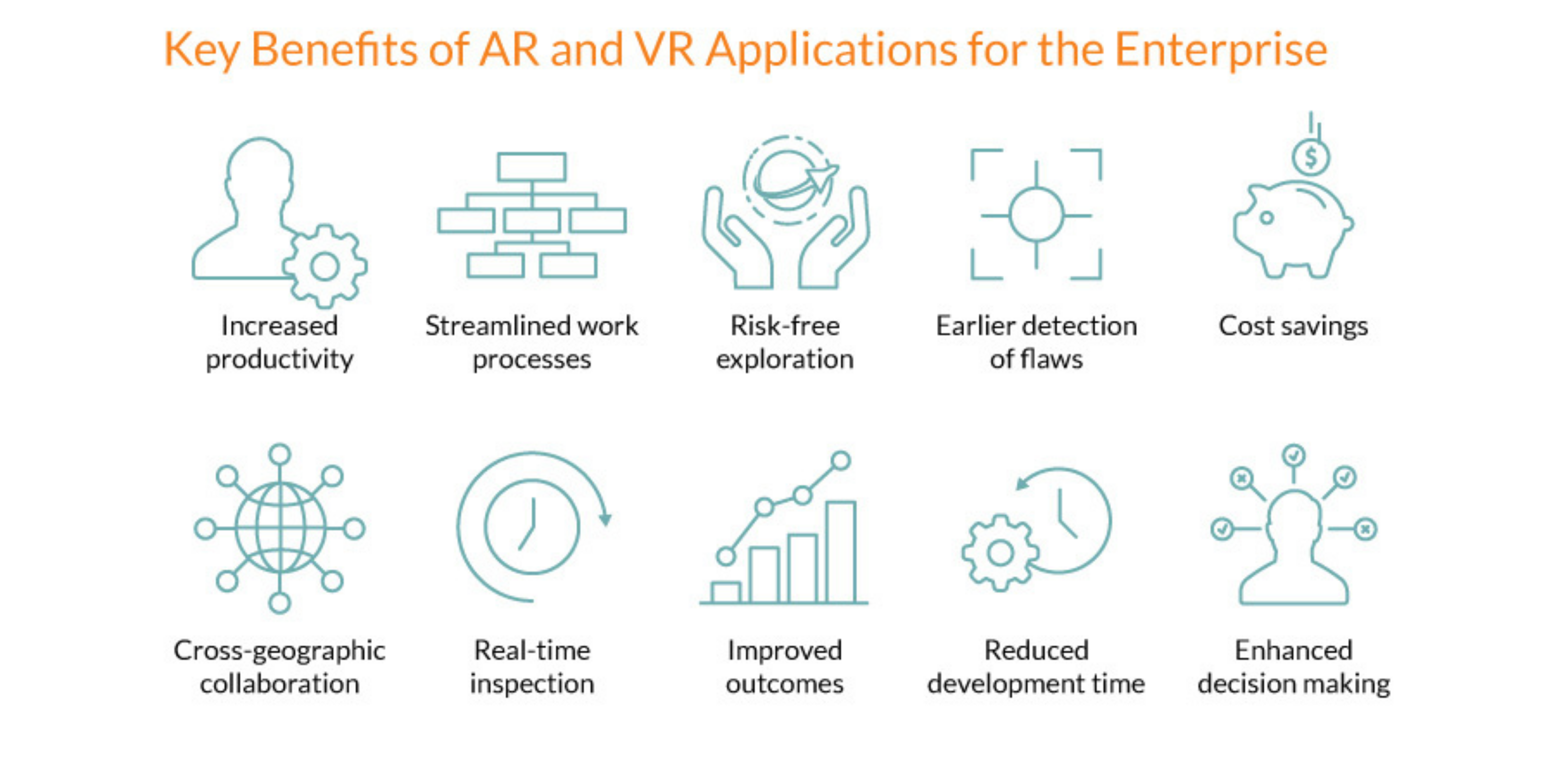
Applications of Virtual Reality
Virtual Reality in Gaming
Virtual Reality has revolutionized the gaming industry, offering gamers a level of immersion and interactivity never seen before. With VR, gamers can step into the shoes of their favorite characters and explore virtual worlds in a way that was once unimaginable.

- Revolutionizing gaming experiences
- Virtual worlds and interactive gameplay
- VR hardware and accessories for gaming
Virtual Reality in Education and Training
VR has tremendous potential in the field of education and training. Its ability to create realistic simulations and experiential learning environments opens up new possibilities for educators and learners alike.

- Simulations and experiential learning
- VR in medical training
- Enhancing classroom education with VR
Virtual Reality in Healthcare
In the healthcare industry, VR is proving to be a valuable tool for various applications, from pain management and rehabilitation to surgical training and mental health therapy.

- Pain management and rehabilitation
- Surgical training and remote assistance
- VR therapy and mental health applications
Understanding Augmented Reality
Definition and Concept of Augmented Reality
Augmented Reality (AR) refers to the integration of digital information and virtual elements into the user’s real-world environment. AR enhances the user’s perception of reality by overlaying computer-generated images onto the physical world.
A brief history of Augmented Reality
The concept of Augmented Reality has been around since the early 1990s. It gained mainstream attention with the advent of smartphones and the popularization of AR applications like Pokémon Go. Since then, AR has continued to evolve and find applications in various industries.
How does Augmented Reality work?
Augmented Reality works by utilizing cameras, sensors, and software algorithms to detect and track the user’s environment. Digital information is then overlaid onto the real-world view, creating an augmented experience.

Overlaying digital information on the real world
AR overlays digital information, such as images, videos, and 3D models, onto the user’s real-world view. This can be achieved through various devices, including smartphones, tablets, and specialized AR headsets.
Different types of AR technologies
- Mixed Reality (MR): This type of AR blends the virtual and real worlds seamlessly, allowing users to interact with virtual objects as if they were part of the real world.
- MR devices and applications: Devices like Microsoft HoloLens and Magic Leap One offer mixed reality experiences, with applications ranging from gaming and entertainment to industrial design and training.
Applications of Augmented Reality
Augmented Reality in Entertainment
AR has significantly transformed the entertainment industry, offering enhanced live performances, interactive events, and immersive experiences in movies and television.
- Enhanced live performances and events
- AR in movies and television
- Augmented reality gaming experiences
Augmented Reality in Architecture and Design
AR has revolutionized the architecture and design industries by allowing professionals to visualize architectural models, create 3D spatial plans, and enhance interior design processes.
- Visualizing architectural models
- 3D modeling and spatial planning
- AR in interior design and home improvement
Augmented Reality in Retail and E-commerce
AR has become increasingly popular in the retail and e-commerce sectors, offering virtual try-on experiences, AR shopping, and enhanced product visualization.
- Virtual try-on and fitting rooms
- AR shopping experiences
- Enhancing product visualization and purchase decisions
Virtual Reality vs. Augmented Reality: A Comparison
While VR and AR share the goal of enhancing reality with computer-generated elements, they differ in their technology, user experience, and applications.

Differences in technology and user experience
- VR completely immerses the user in a virtual environment, while AR enhances the real world with virtual elements.
- VR typically requires specialized headsets, motion sensors, and extensive computing power, while AR can be experienced through smartphones or dedicated AR devices.
- VR offers a fully immersive experience, whereas AR maintains user awareness of the real world.
Advantages and limitations of VR and AR
- VR allows for complete immersion and can offer highly realistic experiences, while AR enhances real-world situations with informative and interactive elements.
- VR may cause motion sickness and discomfort due to its immersive nature, while AR has fewer physical side effects.
- VR requires a dedicated physical space, while AR can be experienced anywhere with the necessary device.
Synergies and potential integration of VR and AR
While distinct technologies, VR and AR can work together to create unique experiences. Mixed Reality (MR) devices, for example, combine elements of both VR and AR, offering users the ability to interact with virtual objects in their real-world environment.
The Future of VR and AR
As VR and AR technologies continue to evolve, their potential impact on various industries and society as a whole is significant. Current trends and advancements indicate a promising future for these immersive technologies.

Current trends and developments in VR and AR
Advancements in hardware and software, such as improved displays, better tracking systems, and more sophisticated algorithms, are making VR and AR experiences more realistic and accessible to a broader audience. Additionally, there is a growing interest in integrating VR and AR with other emerging technologies like artificial intelligence and 5G connectivity.
Predictions for the future of VR and AR
The future of VR and AR holds immense possibilities. With advancements in hardware, software, and content creation, it is likely that VR and AR will become more prevalent in various industries, including healthcare, education, and entertainment. Furthermore, increased affordability and accessibility will bring VR and AR experiences to a larger consumer base.

Implications for various industries and society as a whole
The impact of VR and AR on various industries is already being felt, with significant advancements in gaming, education, healthcare, and more. VR and AR have the potential to transform how we learn, work, and entertain ourselves. Moreover, they can bridge geographical gaps, promote creativity, and offer unique solutions to societal challenges.
Frequently Asked Questions
- Oculus Quest 2
- HTC Vive
- PlayStation VR
- Prolonged use of VR can lead to motion sickness, eye strain, and disorientation.
- AR devices, being less immersive, have fewer health concerns.
- VR creates realistic simulations for experiential learning.
- AR provides interactive and informative elements in real-world scenarios.
- VR requires dedicated hardware and physical space.
- AR experiences may depend on the quality of tracking and environmental conditions.
- Gaming and entertainment
- Education and training
- Healthcare and rehabilitation
- Architecture and design
- Retail and e-commerce
Conclusion
In conclusion, Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR) are cutting-edge technologies that have revolutionized various industries. VR immerses users in computer-generated environments, providing realistic experiences, while AR overlays digital information onto the real world. Both VR and AR offer diverse applications, from gaming and entertainment to education and healthcare. The future of VR and AR looks promising, with continuous advancements and increasing integration with other emerging technologies.